Book Review: The RMB In The Global Economy, By Yin-Wong Cheung
In this newly published volume, Yin-Wong Cheung
“discusses the global role of the RMB. After recapitulating its economic and trade growth experiences, we recount China’s evolving exchange rate policy in the post-reform era, review the debate over whether the RMB is overvalued or undervalued, present China’s policies to globalize the RMB, describe offshore RMB trading, assess the current global status of the RMB, and discuss geopolitical tensions in the last few years.

Since 2009, the process of globalizing RMB has not been smooth sailing and has progressed quite unevenly over time. Despite the strong performance in the early 2010s, the RMB is underrepresented in the global market and its global role does not match China’s economic might. The path of RMB internationalization is affected by both China’s economic performance and
geopolitical factors.”
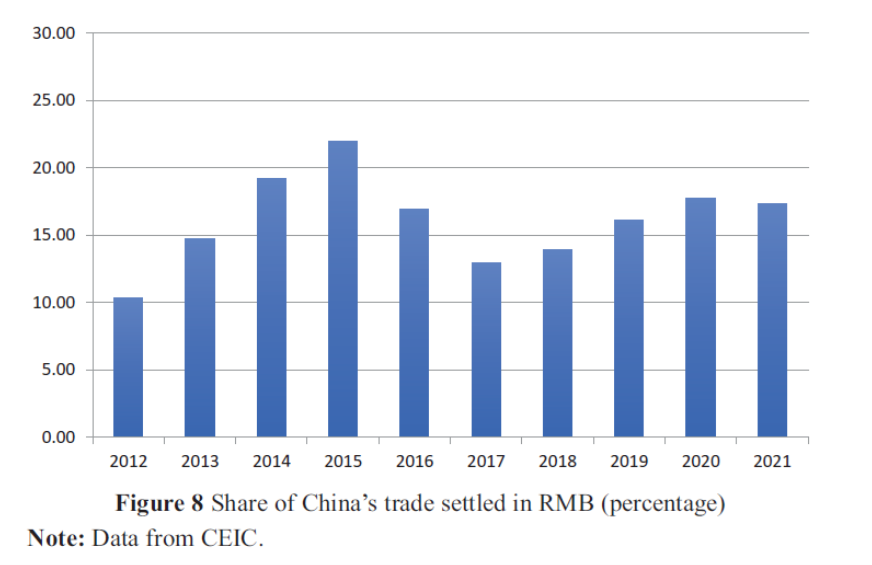
Regarding RMB internationalization, Cheung notes:
After reaching the 2015 high point, the process of globalizing the RMB has progressed quite unevenly and, in some areas, has even reversed. The change occurred in parallel with China’s heightened (administrative) foreign exchange management, financial deleveraging policies, and the concurrent increase in global uncertainty and geopolitical tensions that have decreased global demand for RMB-denominated assets. Further, the eruption of the China-US trade dispute and the subsequent change in the view toward China do not favor the international use of the RMB. The 2020 coronavirus pandemic presented China with another chance to regain the momentum of globalizing its currency. The pandemic impacted China hard in the first half of 2020; however, with its effective public health control measures, China demonstrated its economic resilience in late 2020 and 2021.32 This speedy economic recovery and the RMB’s stability have improved the attractiveness of RMB-denominated assets to international investors and enhanced the global usage of the RMB.
In the following subsections, we recount China’s main policies for promotion of RMB internationalization and discuss its outsourcing practice – the offshore RMB trading. China’s RMB internationalization program covers and interacts with a wide range of topics. While a complete coverage of RMB international-ization is beyond the scope of this study, we offer an overview.
Source: Cheung (2022).
Any scholar wishing to follow China’s policies regarding its exchange rate must read this volume.
My thoughts on previous essays on China’s currency include Eswar Prasad’s Gaining Currency (2015), Paulo Subacchi’s The People’s Money (2017). My take on the RMB’s status relative to the dollar was presented at a recent Board-NY Fed conference.
If the author’s name sounds familiar, he (along with myself and Eiji Fujii) coauthored The Economic Integration of Greater China (2007) (we’re working on an update now), several works on RMB misalignment (most recently, Cheung, Chinn and Xin, 2017), exchange rate prediction (most recently Cheung, Chinn, Garcia Pascual, Zhang, 2019), and on Chinese imports and exports (Cheung, Chinn, Qian, 2015).
More By This Author:
Did The Yield Curve Predict A 2022H1 Recession?
Term Spread Recession Forecasts
How To End An Endless Debate