Powell: Inflation Might Not Be Transitory, After All
At a panel discussion, Fed Chair finally admitted that inflation could be more (!) long-lasting than expected. What does it mean? Hawks. Lots of them.
Capitulation
With Fed Chairman Jerome Powell finally having his ‘come-to-Jesus’ moment on Sep. 29, the central bank chief’s skittish words helped light a fire under the USD Index. For context, I’ve been warning for months that Powell remains materially behind the inflation curve. And with his indecisive speech upending the Fed’s confidence game, the gambit is showing signs of unraveling.
Speaking at an ECB panel discussion on Sep. 29, he said:
“The current inflation spike is really a consequence of supply constraints meeting very strong demand. And that is all associated with the reopening of the economy, which is a process that will have a beginning, middle and an end. It’s very difficult to say how big the effects will be in the meantime or how long they last.”
For context, first, it was “base effects,” then it was “transitory” and now “it’s very difficult to say.”
He continued:
“It’s also frustrating to see the bottlenecks and supply chain problems not getting better – in fact, at the margins apparently getting a little bit worse. We see that continuing into next year probably, and holding up inflation longer than we had thought.”
What’s more, Powell actually admitted that the Fed is facing a conundrum that it hasn’t dealt with “for a very long time.”
“Managing through that process over the next couple of years is… going to be very challenging because we have this hypothesis that inflation is going to be transitory. We think that’s right. But we are concerned about underlying inflation expectations remaining stable, as they have so far.”
Wow. If that’s not capitulation, I don’t know what is.
For context, I wrote on Sep. 24:
I’ve warned on several occasions that the only way for the Fed to control inflation is to increase the value of the U.S. dollar and decrease the value of commodities. However, with commodities’ fervor accelerating on Sep. 23 – a day when the USD Index declined – the price action should concern Chairman Jerome Powell. As a result, FOMC participants’ 2022 inflation forecast is likely wishful thinking and they may find that a faster liquidity drain (which is bullish for the U.S. dollar) is their only option to control the pricing pressures.
Speaking of which, the S&P Goldman Sachs Commodity Index (S&P GSCI) has rallied by ~5% for the month of September. For context, the S&P GSCI contains 24 commodities from all sectors: six energy products, five industrial metals, eight agricultural products, three livestock products, and two precious metals. However, energy accounts for roughly 54% of the index’s movement.
Please see below:
(Click on image to enlarge)
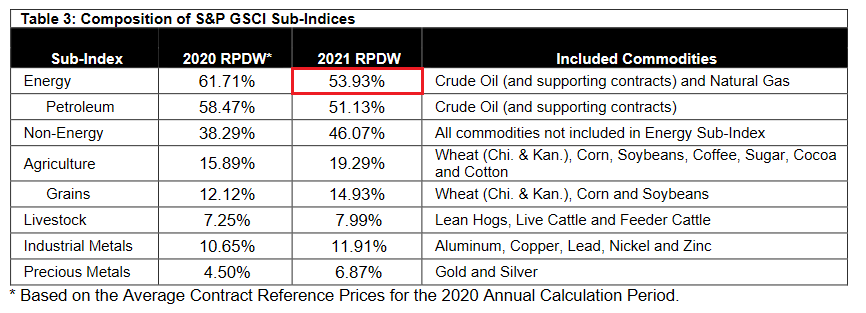
Source: S&P Global
As well, if you analyze the graphic below, you can see the impact that rising energy prices had on the S&P GSCI’s performance in September (MTD returns as of Sep. 27).
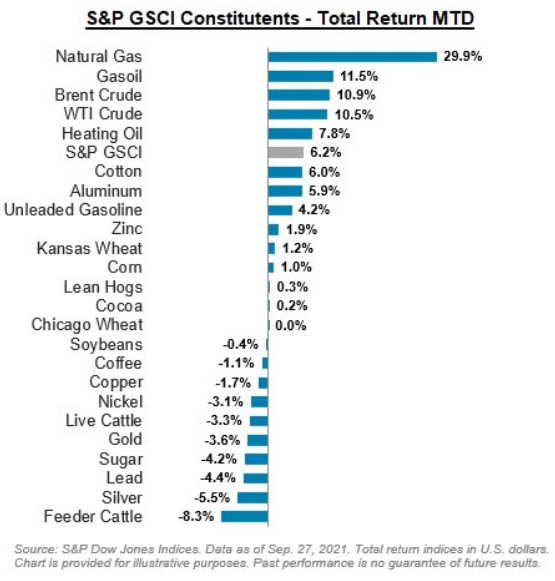
To that point, with Brent and WTI surging recently and the latter on track for six straight weeks of weekly gains, Goldman Sachs has upped its year-end Brent target to $90 a barrel. Calling it the “revenge” of the old economy, Jeff Currie, Goldman Sachs global head of commodities research, said that “poor returns saw capital redirected away from the old economy to the new economy. It’s not unique to Europe, it’s not unique to energy, it’s a broad-based old-economy problem.”
Thus, in his view, commodity prices need to be “much higher to get returns sufficient to start attracting capital. People wanted a quick return, and now you’re paying the price for it.”
Please see below:

Supporting the thesis, Bank of America commodities strategist Francisco Blanch told Bloomberg on Sep. 28 that Brent could hit $100 a barrel in 2022 and that a “cold winter” could actually pull forward the forecast.
He said:
“First, there is plenty of pent up mobility demand after an 18 month lockdown. Second, mass transit will lag, boosting private car usage for a prolonged period of time. Third, pre-pandemic studies show more remote work could result in more miles driven, as work-from-home turns into work-from-car. On the supply side, we expect government policy pressure in the U.S. and around the world to curb cap-ex over coming quarters to meet Paris goals. Secondly, investors have become more vocal against energy sector spending for both financial and ESG reasons. Third, judicial pressures are rising to limit carbon dioxide emissions. In short, demand is poised to bounce back and supply may not fully keep up, placing OPEC in control of the oil market in 2022.”
Now, the important point isn’t whether or not Currie and Blanch are correct. The important point is that higher oil prices are mutually exclusive to Powell’s 2% inflation goal. For example, the Commodity Producer Price Index (PPI) – which is a reliable indicator of the next month’s Consumer Price Index (CPI) – recorded its highest monthly year-over-year (YoY) percentage increase in August since 1974. What’s more, the sky-high reading occurred with the S&P GSCI declining by ~2% in August (that’s why monitoring surging container rates is so important). However, as mentioned, the S&P GSCI has already risen by ~5% in September and container rates have also made new highs. As a result, Powell’s hawkish shift isn’t nearly hawkish enough to solve his inflationary dilemma.
Inflation Isn’t Going Anywhere
As further evidence, the Richmond Fed released its Fifth District Survey of Manufacturing Activity on Sep. 28. And while the headline index turned negative as output slumped, pricing pressures remained materially elevated.
Please see below:
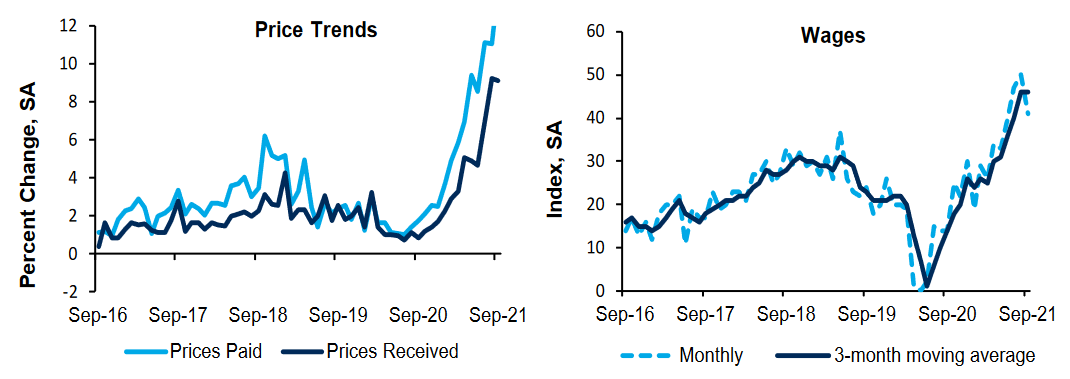
Source: Richmond Fed
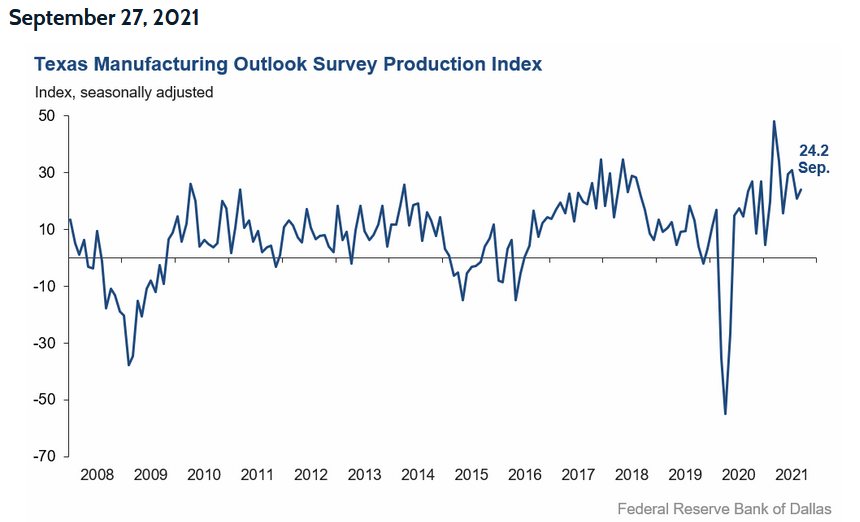
Likewise, the Dallas Fed released its Texas Manufacturing Outlook Survey on Sep. 27. The report revealed:
“Prices and wages continued to increase strongly in September. The price indexes climbed further, with the raw materials prices index at 80.4 and the finished goods prices index at 44.0, an all-time high. The wages and benefits index held steady at a highly elevated reading of 42.7.”
For a visual of the overall index, please see below:
Furthermore, the Dallas Fed also released its Texas Service Sector Outlook Survey and its Texas Retail Outlook Survey on Sep. 28. And though the U.S. service sector has suffered the brunt of the Delta variant’s wrath, pricing pressures remained. The report revealed:
“Wage pressures eased in September, though remained at historically high levels, while price pressures remained highly elevated. The wages and benefits index declined from 32.6 to 26.9. The selling prices index was largely unchanged at 20.2, with nearly a quarter of firms reporting increased prices compared with August, while the input prices index inched up one point to 42.9.”
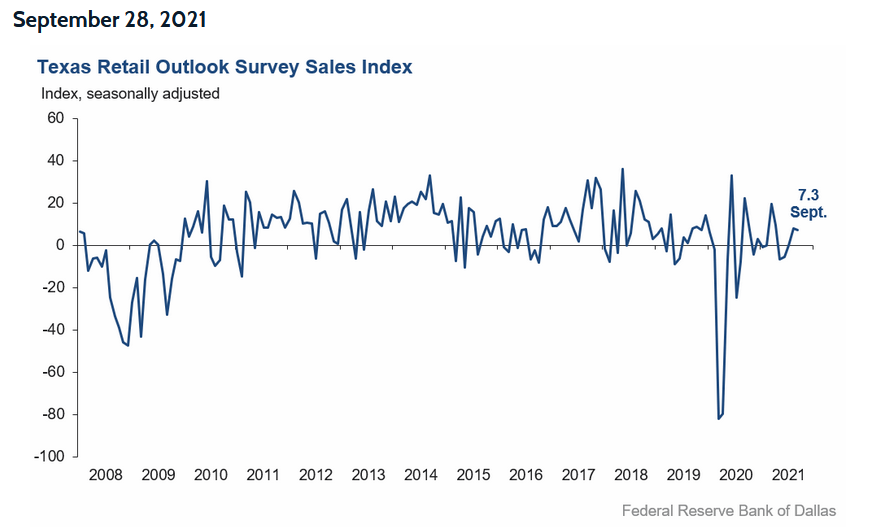
More importantly, though, the Texas Retail Outlook Survey revealed:
“Retail price pressures surged once again in September after some signs of moderation in August, while wage pressures held steady. The selling prices index surged nearly 11 points to 50.4 – with 58 percent of retailers increasing prices compared with August – while the input prices index increased from 41.3 to 50.1. The wages and benefits index was flat at 24.6.”
For a visual of the overall index, please see below:
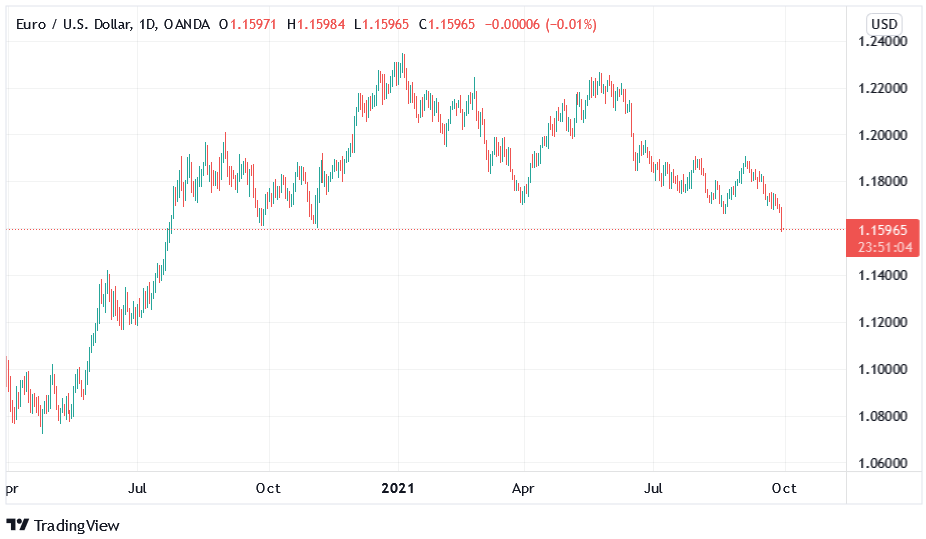
And as the drama unfolds and Powell’s inflationary conundrum intensifies, his hawkish rhetoric on Sep. 29 helped sink the EUR/USD. For context, the EUR/USD accounts for nearly 58% of the movement of the USD Index. And with the currency pair collapsing below 1.1600 on Sep. 29 and closing below key 2020 support, the European dam could be about to break.
Please see below:
Reverse Repos Hit Another All-Time High!
Also bullish for the U.S. dollar, with Powell’s liquidity circus still on full display, there is too much money floating around with too little use. And upping the ante on what I’ve been highlighting for months, after 80 counterparties drained nearly $1.416 trillion out of the U.S. financial system on Sep. 29, the Fed’s daily reverse repurchase agreements hit another all-time high.
Please see below:
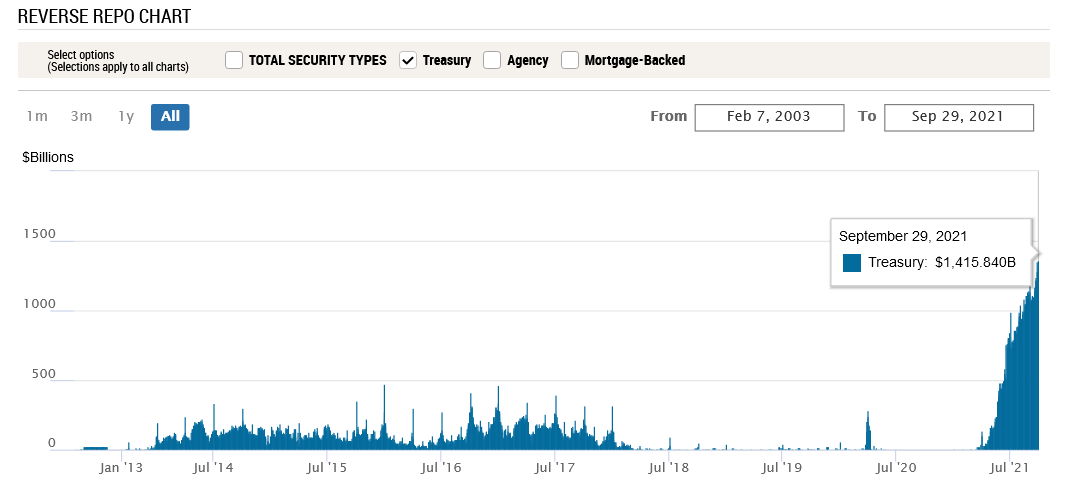
Source: New York Fed
To explain, a reverse repurchase agreement (repo) occurs when an institution offloads cash to the Fed in exchange for a Treasury security (on an overnight or short-term basis). And with U.S. financial institutions currently flooded with excess liquidity, they’re shipping cash to the Fed at an alarming rate. I’ve been warning for months that the activity is the fundamental equivalent of a taper due to the lower supply of U.S. dollars (which is bullish for the USD Index). Thus, while we await a formal announcement from the Fed, the U.S. dollar’s fundamental foundation remains robust.
The bottom line? Powell’s only hope to curb inflation is to strengthen the U.S. dollar and weaken commodity (including gold and silver) prices. For context, major futures contracts are priced in U.S. dollars. And when the dollar rallies, it’s more expensive for foreign buyers (in their currency) to purchase the underlying commodities. As a result, a stronger U.S. dollar often stifles demand. And with the current supply/demand dynamics favoring higher commodity prices, Powell will have to work his magic — strengthen the dollar and reduce demand — if he wants his inflation problem to subside.
In conclusion, gold, silver (ouch), and mining stocks sunk like stones on Sep. 29. And with the USD Index cutting through 94 like a knife through butter, new 2021 lows in the EUR/USD were accompanied by new 2021 highs in the USD Index. Moreover, with the momentum poised to continue, the PMs’ medium-term outlooks remain quite somber. As a result, further weakness will likely materialize before brighter days emerge (probably) near the end of the year.
Disclaimer: All essays, research and information found on the Website represent the analyses and opinions of Mr. Radomski and Sunshine Profits' associates only. As such, it may prove wrong ...
more










