Gold: U.S. Debt Surpasses $31 Trillion

Image Source: Pexels
The U.S. National Debt
The United States has a significant amount of national debt, which is the total amount of money owed by the federal government. As of April 30, 2023, the U.S. national debt stands at over $31 trillion, which is equivalent to around 107% of the country's Gross Domestic Product (GDP). This debt has been growing steadily for many years, driven primarily by government spending that exceeds tax revenues.
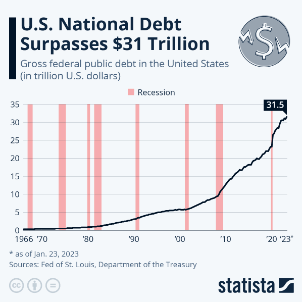
debt (statista)
The U.S. government issues Treasury bonds to finance its debt, which are sold to investors both domestically and internationally. Interest payments on these bonds are a significant portion of the government's annual budget and will continue to be so in the foreseeable future.
The reasons for the high national debt include government spending on social programs, defense, and interest payments on existing debt. Some experts argue that the debt is unsustainable in the long run and may have negative economic consequences, such as higher interest rates, inflation, and reduced economic growth.
However, others argue that some level of government debt is necessary to support economic growth and stability. They also point out that the U.S. government's ability to borrow at low interest rates is a sign of confidence in the country's financial stability and economic prospects.
Overall, managing the national debt is a complex and ongoing challenge for the U.S. government, and there is ongoing debate about how best to address it in the short and long term.
Interest Payments and the U.S. Debt
The U.S. national debt affects the interest payments of the U.S. Treasury in a few different ways.
Firstly, as the national debt increases, so does the amount of interest that the U.S. government must pay to investors who hold U.S. Treasury bonds. This is because the U.S. Treasury must pay interest on the bonds it issues, and the larger the amount of debt, the more interest payments are required.
Secondly, the interest rate that the U.S. Treasury must pay on its bonds can be influenced by the level of demand for those bonds. If there is strong demand for U.S. Treasury bonds, the interest rate that the government must pay to attract investors may be lower. Conversely, if demand for U.S. Treasury bonds is weak, the government may need to offer a higher interest rate to attract investors.
Finally, the level of interest rates in the broader economy can also affect the interest payments of the U.S. Treasury. If interest rates in the economy as a whole rise, the U.S. Treasury may need to pay higher interest rates to investors to remain competitive.
Overall, the U.S. national debt can have a significant impact on the interest payments made by the U.S. Treasury, and managing the debt is an important part of the government's overall economic strategy.
However, according to the U.S. Treasury Department's most recent data, the U.S. government's net interest payments on its outstanding debt totaled approximately $522 billion in fiscal year 2021, which ended on September 30, 2021. This represents a significant portion of the federal government's overall spending, accounting for roughly 8% of total federal outlays for the year. The amount of net interest payments made by the U.S. government can vary from year to year, depending on a variety of factors, including the level of outstanding debt, prevailing interest rates, and the terms of the government's borrowing.
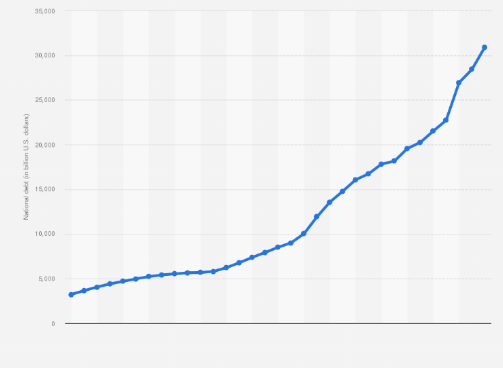
debt (statista)
In September 2022, the national debt of the United States had risen up to 30.93 trillion U.S. dollars. The national debt per capita had risen to 85,552 U.S. dollars in 2021. As represented by the statistic above, the public debt of the United States has been continuously rising.
U.S. Debt and the price of Gold
There is a complex and multifaceted relationship between the U.S. national debt and the price of gold, which is a popular investment and hedge against economic uncertainty.
On the one hand, a high level of national debt can lead to concerns about the long-term economic health of the U.S., which may lead some investors to seek out alternative investments such as gold. This can create upward pressure on the price of gold, particularly during times of economic uncertainty or geopolitical instability.
Additionally, high levels of government spending and debt can sometimes lead to inflation concerns, as the government may need to print more money or raise interest rates to manage the debt. This can also drive up demand for gold as a hedge against inflation, further boosting the price of the precious metal.
However, the relationship between the U.S. national debt and the price of gold is not always straightforward or predictable. Other factors, such as global economic trends, currency fluctuations, and geopolitical events can also impact the price of gold, and the relationship between gold and the national debt can vary depending on the specific circumstances.
In summary, while there is a connection between the U.S. national debt and the price of gold, it is just one of many factors that can influence the price of the precious metal, and the relationship between the two is complex and multifaceted.
As traders in the gold market, we employ the use of standard deviation to gain insight into the long-term outlook of the market. We analyze the 360-day cyclical patterns, as well as monthly and weekly patterns, to provide a comprehensive report that we publish in the marketplace section under mean reversion trading. In this month's report, we focus on the monthly gold standard deviation and identify potential trading opportunities for the coming month. By analyzing the market trends and applying our expertise in mean reversion trading, we aim to provide valuable insights that can help traders make informed decisions.
More By This Author:
An Inverted Yield Curve And The Price Of Gold
Retail Apocalypse: Gold And Silver Bottoms
Gold: A Race To The Bottom
Disclosure: I/we have no stock, option or similar derivative position in any of the companies mentioned, and no plans to initiate any such positions within the next 72 hours.
Disclaimer: The ...
more


