The Bank Of Canada Will Drop Anchor At A 3% Bank Rate
Behavioral economists have long warned policymakers of the dangers of “anchoring” on a specific number. So often, we anchor or latch onto a specific economic number which then we use to establish rules to make decisions regarding policy. Central bankers, for example, have anchored on the goal of 2% inflation and all decisions regarding interest rates are aimed at allowing the economy to expand while not exceeding that inflation target.
Made famous by Nobel prize winner in economics, Daniel Kahneman[1], anchoring has now become a well-documented tool used by behavioral economists to explain decision- making. What happens when the number we anchor upon turns out to be a poor choice for the purpose of making a whole set of decisions affecting the financial markets and the economy in general?
Governor Poloz of the Bank of Canada has been telling Canadians to get ready for a bank rate of 3%. He is anchoring on that number based upon a concept of the “neutral rate of interest” [2] which is also touted by the Federal Reserve. The neutral rate can be considered as a benchmark to gauge the degree of monetary stimulus in place. If the bank rate is below the neutral rate, then monetary policy is considered to be simulative; above the neutral rate, monetary policy is restrictive. The Bank of Canada has set the neutral rate between 2.5% and 3.5% and for the purposes of building their projections, a 3%neutral rate is adopted.
The Governor argues that wages will grow faster as the labor market tightens and the economy operates at full capacity. However, it is not at all evident that wages will accelerate. Inside Canada’s October job report, hourly earnings eased to a 1.9% y/y growth rate from 2.2% in September, continuing the slowdown in wage growth started in the spring of this year (see accompanying chart). A deceleration in wage growth is not supportive of a position that rate hikes are needed and that we should anchor on reaching the target of 3%. Moreover, wage growth should be examined in terms of labor costs per unit of output. Unit labor costs in Canada have plateaued earlier in the year and also have tended to decelerate.
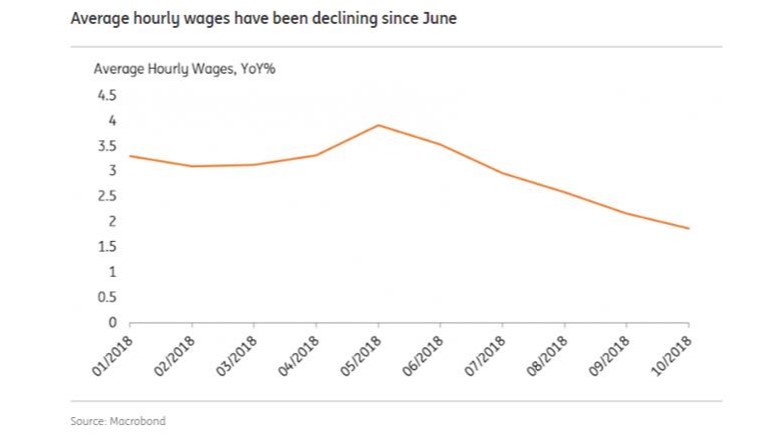
Finally, the October jobs numbers revealed no gains in employment and no change in the unemployment rate of 5.8%. Over the past 12 months, the number of employed workers grew just by 1.1%, hardly an indication that the demand for labor is growing and that wages are about to accelerate. Over the same period, total hours worked rose by a mere 0.7%, another sign of a relatively tame labor market. None of these data suggest that there is or will likely be a surge in wage growth that will spark inflation.
Anchoring often can lead to policy errors.
[1] Thinking Fast, Slow, Farrar, Straus and Giroux,2011
[2] The Bank Of Canada Holds Out For A ‘Neutral’ Rate Of Interest




I wonder how central banks weigh wages against asset inflation in determining what is loose and what is tight. Seems like wages take center stage. Labor takes a beating most times.
I think you are right on the mark. No central banker worried about P/E in tech stocks in the 100.But heaven forbid that wages grow at 4% the bond yields soar.