Iron Ore Slump Shows Chinese Economy Is Still Struggling

A remote-controlled shovel loader works underground at an iron mine in northeast China's Liaoning Province
China’s economic recovery falters
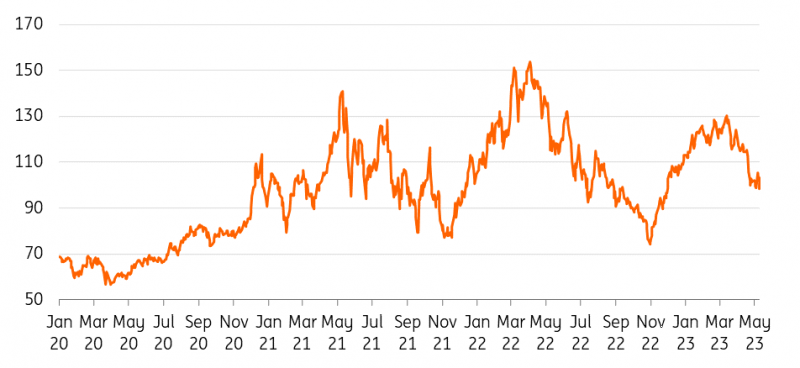
Iron ore has been on a downtrend for almost two months. Its price on the Singapore Exchange fell to a year-to-date low of $94.20/t last week, down more than 20% from its year-to-date highs and is now hovering below the key $100/t level.
Prices climbed above $130/t in February amid bets of a revival in steel demand in leading consumer China following the end of the strict Covid-19 lockdowns.
Although China last month reported annual quarterly GDP growth of 4.5%, ahead of expectations - and much faster than the 2.9% for Q422 - there are concerns about whether the pace of growth can be sustained. China’s manufacturing activity slowed in April, with the Purchasing Managers’ Index falling from 51.9 in March to 49.2 in April, a warning signal to the Chinese economy. This followed three straight months of growth since the start of 2023.
The growth in the construction sector, which accounts for about half of Chinese steel demand, has also been slower than anticipated. New property starts in March were down 29.1% compared with the same period the previous year.
Meanwhile, consumer inflation in China dropped close to zero in April, and its weakest pace in two years, while producer prices fell further into deflation, adding to concerns over a weak demand recovery in the country.
Iron ore slides below $100/t
China's steel consumption disappoints
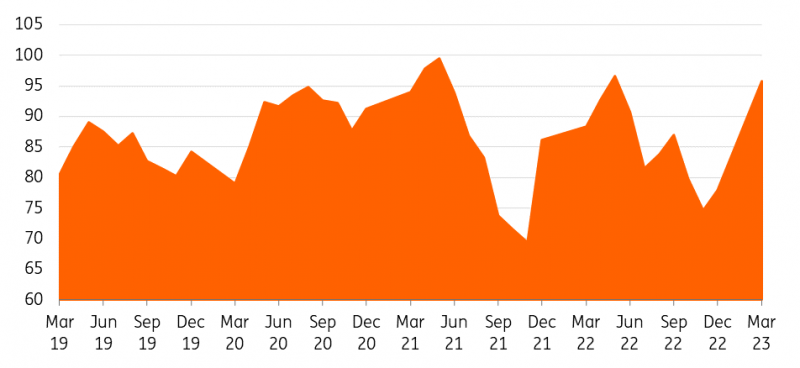
Steel consumption in China has disappointed during what is normally a peak construction season in the country. March and April are usually peak production months for the Chinese steel market. Recent data from the China Iron and Steel Association (CISA) show that steel inventories at major Chinese steel mills fell to 18.1mt in late April, down 2.3% compared to mid-April.
Similarly, crude steel production at major mills decreased by 3.6% in the period to 2.21mt/d in late April.
Amid disappointing demand, steel mills have been forced to reduce prices to offload volumes. China Baowu Steel, China’s top steel producer, lowered its factory-gate prices, along with at least two other mills, according to Mysteel. Meanwhile, steel mills in the Fengnan district of Tangshan City have been officially asked by the local authorities to curb crude steel output. This would be the first batch of steel mills in China to observe another administrative year-on-year reduction in crude steel output after repeated cuts in 2021 and 2022.
Chinese authorities are reportedly considering an official target of lowering steel output by 2.5% in 2023.
China’s steel production dropped 2% last year to 1.0bn tonnes, according to data from the World Steel Association, mainly due to government-mandated production cuts.
It appears that China will continue to cap crude steel output whilst also looking to replace older steel capacity with electric arc furnace capacity in order to help the country meet its decarbonisation goals. Growth in electric arc furnace (EAF) capacity at the expense of basic oxygen furnace (BOF) capacity will be a concern for the medium to long-term outlook for Chinese iron ore demand. It also suggests that we have already seen China’s iron ore imports peak in 2020.
China monthly crude steel output (million tonnes)
China's iron ore imports slow down
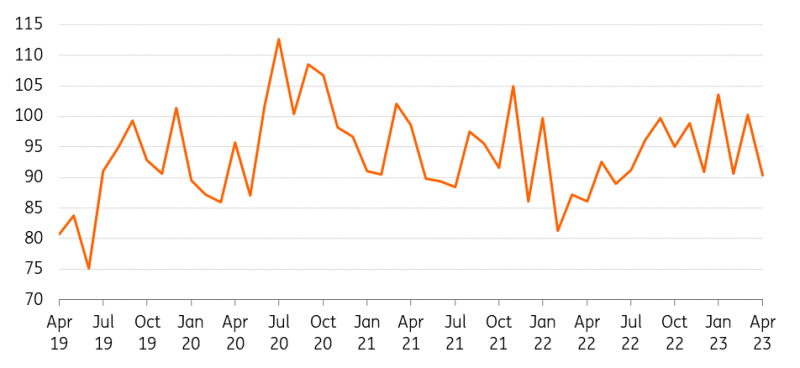
Amid lower steel consumption from China, iron ore imports have also been under pressure this year. Chinese purchases of iron ore slumped to a 10-month low in April, in a sign of waning demand.
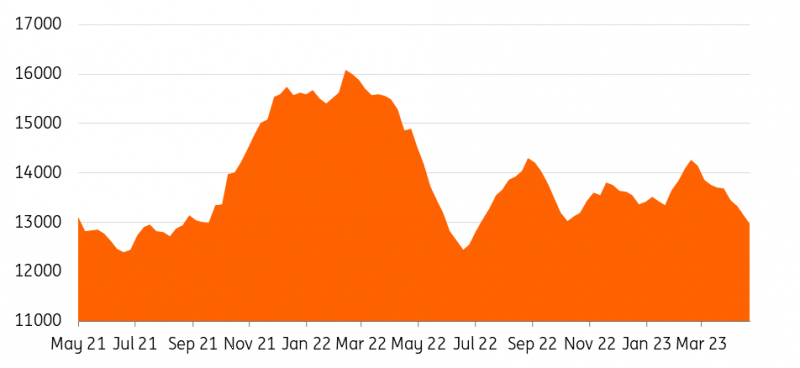
China imported 90.44 million tonnes of iron ore in April, down more than 100 million tonnes in March and the least since June 2022, customs data show. Iron ore inventories have also been falling. Total iron ore stockpiles across ports in China are down 11% year-on-year at 129.2m tonnes. China’s iron ore port inventory is a key indicator that reflects the supply and demand balance, as well as the safety net and imbalance between the iron ore supply and the steel mill demand.
With the peak construction season coming to an end and with the expected demand recovery not meeting expectations, there is little upside for steel output and iron ore demand recovery in the short to medium term.
China monthly iron ore imports (million tonnes)
China iron ore total ports inventory (10000 metric tonnes)
Supply from majors ramps up
The supply side has been firm so far this year. Rio Tinto, the world’s biggest iron ore producer, reported a better-than-expected 15.4% jump in Q1 iron ore shipments from Western Australia, a record for the quarter, as production at its Gudai-Darri mine ramped up. Its Pilbara operations produced 79.3 million tonnes of iron ore in Q1 of 2023, 11% higher than the Q1 of 2022.
Also, Vale SA reported a 5.8% year-on-year increase in Q1 iron ore production due to stronger performance at S11D. The company produced 66.77 million tonnes of iron ore during the first three months of 2023.
Meanwhile, BHP has maintained its iron ore production guidance at between 249 million to 260 million tonnes in the full year after reaching a record 191.7 million tonnes iron ore production year-to-date, with the March quarter contributing 59.8 million tonnes.
Government scrutiny could cap prices
Sharp price movements in iron ore have drawn scrutiny and warnings from regulators. The National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) said last month that it would closely monitor iron ore market dynamics and take steps to limit price hikes. Since the start of the year, the NDRC and other authorities have been enhancing the collaborative supervision and regulation of the iron ore market and have cracked down on price gouging, excessive speculation, and illegal activities.
Previously, government interventions to calm the markets have included subduing trading and ordering steel capacity cuts. If we see similar measures used again, this could add further downside pressure to our view.
We believe the short-term outlook remains bearish for iron ore, with sluggish demand from China suggesting that prices should trend lower. We expect prices to average $100/t in Q4 and $106/t in 2023, and prices will remain volatile as the market will continue to be responsive to any policy change from the Chinese government.
More By This Author:
Czech Republic: CPI Inflation Edges Below CNB Estimate, Challenging Possible Hike
Bank Of England Hikes Rates And Keeps Options Open For Further Increases
Philippines’ First Quarter GDP Surprises On The Upside But Could Mark The Peak
Disclaimer: This publication has been prepared by the Economic and Financial Analysis Division of ING Bank N.V. (“ING”) solely for information purposes without regard to any ...
more


