ESG Has A Trust Deficit And Here’s Why
![]()
What do we mean by ESG?
Investopedia offers this summary: Environmental criteria consider how a company safeguards the environment, including corporate policies addressing climate change, for example. Social criteria examine how it manages relationships with employees, suppliers, customers, and the communities where it operates. Governance deals with a company’s leadership, executive pay, audits, internal controls, and shareholder rights. The conversations around the role of “S” (how companies treat their stakeholders) and “G” (how they are governed) have recently come into focus and for good reason.
What do we mean by a “trust deficit.”
At Trust Across America-Trust Around the World (TAA-TAW) we consider trust as the “outcome of principled behavior.” If principled behaviors are absent, a trust deficit is created.
What is Causing the ESG Trust Deficit?
Reading the current headlines one might concluded that the ESG trust deficit is “all political.” That one side wants ESG and the other does not, so one group is “right” and the other is “wrong.” But while politicizing ESG may be convenient for some, blaming politics ignores the root causes of the trust deficit (the behavioral ones), and they are plentiful.
The Employee Perspective
According to the Public Affairs Council members of the public don’t trust corporate CEOs as much as they trust the companies these CEOs lead: 47% place a lot of trust or some trust in major companies to behave ethically but give CEOs poor marks in this area. Only 7% believe CEOs have high standards for honesty and ethics, and almost half (47%) believe their standards are low. October 2020
And Gallup recently reported that low employee engagement costs the global economy $8.8 trillion or 9% of global GDP.
The Sustainability Perspective
Elaine Cohen, a leading global voice in sustainability and reporting offers the following:
For me, the ESG Trust Deficit shows up as publicly stating a commitment to ESG but not following through with actions:
- inconsistencies between what the company talks about in its (financial) annual report and its sustainability report
- lack of integration of ESG as part of the business strategy
- lack of clear ESG targets and transparent report of progress against targets while declaring a strategic approach to ESG or sustainability
- lack of understanding of the financial implications of ESG impacts
- public commitment but the poor performance against commitments
- lack of Board understanding and visibility on sustainability matters
- lack of accountability for Board members for ESG matters
The Governance Perspective
Lawrence A. Cunningham an authority on corporate governance, corporate culture, and corporate law has this to say: The traditional “G” in ESG refers to allocation of corporate power among and between directors, officers, and shareholders. The “E & S” (and now the “P” for political) is a nouveau addition addressing allocations of corporate power to other constituencies as well, especially fellow citizens, employees, and customers. Among the pairs between traditional governance and nouveau ESP some are (1) mutually compatible in theory (so both can possibly be implemented without necessarily compromising), (2) mutually exclusive and (3) mutually compatible in theory but often not in practice (the nouveau ES focus crowds out traditional G priorities). The related classifications in the following infographic are subjective judgment rather than scientific truth but they illuminate the changing landscape and stakes.

What does this chart reveal about the role and value of trust? Walking through the exercise and sensing the variability and uncertainty of the practices and priorities will likely raise questions for many readers about the compatibility of the nouveau ESP practices with fundamental notions of trust.
The Leadership Perspective
Finally, Barton (Bart) Alexander who has worked to effect positive change from senior executive positions within government, Fortune 500 corporations, and NGOs weighs in on a third cause of the ESG trust deficit.
The longstanding cycles of labeling and then criticism of the labeling are just in another phase. We used to have corporate citizenship, then corporate responsibility, then shared value, then ESG, then purpose. Each creation of the “new framework” says the old one is misdirected and incomplete. Even governance for a long time was just about the basics of transparency and accountability. In one of the current cycles, we have ESG being criticized as PR oriented, then Woke, and now we have green hushing as much as greenwashing.
Companies are challenged to meet investor expectations amidst pressure to adhere to environmental and social imperatives. Taking a stand exposes them to accusations from both sides — being too slow and prioritizing “woke” issues over profits.
In conclusion, thriving companies adhere to sound business strategies, without succumbing to polarized debates. Their sustained success depends not only on short-term profits but on building value for all of their stakeholders, starting with their employees. They need not exaggerate nor hide what they are doing — their results speak for themselves. Senior executives who make principled behavior a priority tend not to “take stands” or make bold claims via corporate communications about their purpose or the organization’s positive environmental and social programs. Instead, they simply choose to do the right thing without much fanfare.
For Trust AcrossAmerica-Trust Around the World (TAA-TAW) this is not a new revelation. When we built our FACTS® Framework over ten years ago to evaluate the trustworthiness of public companies, we recognized the need to create a holistic model of principled organizational behavior that gave equal weight to the E, S, and G. This was long before ESG became a “household name.” The FACTS® Framework is an acronym that includes five drivers or indicators of trustworthy business behavior. Read more at the link.
One Solution to the ESG Trust Deficit: Trust 200 Index
TAA-TAW maintains an index of our FACTS® Top 200 most trustworthy public companies. The Index is updated daily. The twelve-year performance against two benchmarks (iShares Russell 1000 Value ETF (IWD) and SPDR S&P 500 (SPY) ETF) is shown below (as of August 3, 2023) and the results speak for themselves. Over time the most trustworthy companies outperform.
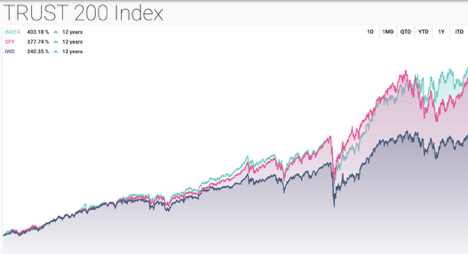
Why? The best leaders create long term value through principled behavior which builds trust instead of breaking it. They know it begins with integrity which enables trustworthy leaders to attract and retain top talent who then willingly owns and model the values flowing from the top. These values then organically tend to extend to all stakeholders. Said another way, trust is built over time and in incremental steps by the actions of trustworthy leaders, not through weak or politicized ESG “programming” or “talk.” The public has watched these misdirected messages backfire time and again, resulting in an accelerating erosion of trust. And this is why the ESG trust deficit exists.
The trustworthiness of an organization is determined equally by its environmental, social, and governance structure and practices, incorporating not only shareholder interests but those of other stakeholders as well, beginning with employees. ESG programs don’t create or fix trust, but principled behavior will do both.
More By This Author:
Trust Challenges & Predictions 2023Trustworthy Companies Offer Superior Investment Returns With Less Risk
Most Trustworthy Public Companies
More information on TAA-TAW can be found at www.trustacrossamerica.com



