Blockchains: Why You Might Not Realize You’re Using Them
Photo by Clint Adair on Unsplash
In our ever-evolving digital ecosystem, understanding the bedrock of digital assets—blockchain technology—is important to understand how they can impact our future and how we might use them.
To help us think about how these technologies might impact us in the future, we can compare blockchain protocols to the internet protocols we use every day. While almost everyone can send an email, few can explain how it works.
Two of those internet protocols we use every day are SMTP and HTTP.
Companies like Google and Microsoft employ SMTP for their email services, while web browsers make use of HTTP for us to browse the internet and view webpages. For all but a small percentage of users, we don’t understand the protocols or realize we’re using them.
The same might end up being true for blockchain technologies and digital assets.
Let’s demystify these complex systems and show how they operate on similar principles to help explain why we might not even know we’re using blockchain technologies in the future.
Unraveling the Blockchain Layers
(Click on image to enlarge)
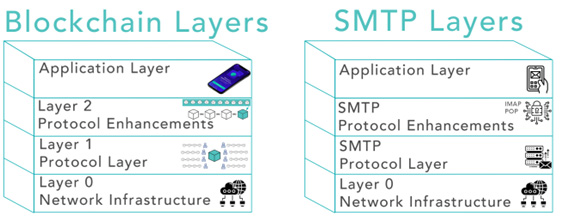
You can think of blockchains as layers that stack on top of each other. Each layer adds more functionality to the system, building up from the very basic physical infrastructure to the applications that we see and interact with. Let’s start with the bottom layers.
1. Layer 0 – Network Infrastructure: This is the foundation of any digital system, blockchains included. It consists of the physical hardware (servers, routers, cables) and the internet protocols that handle data transmission, like TCP/IP.
2. Layer 1 – Protocol Layer: Here lives the heart of blockchain—the blockchain protocol. It sets the rules of the network, such as how transactions are validated and how consensus is reached. Examples are Bitcoin and Ethereum.
3. Layer 2 – Protocol Enhancements: These are enhancements to the base protocol designed to improve its functionality, speed and efficiency. This is where you’ll find solutions to the issues that plague many blockchains. These protocols or technologies are built on top of specific layer 1 blockchains.
4. Application Layer: This is the layer we interact with. It’s the user-facing applications—wallets, exchanges and decentralized applications (dApps)—that allow us to use blockchain technologies without needing to understand the intricate technical details.
Some applications are built directly on top of Layer 1 blockchains, but this might not be the best setup because of the disadvantages of Layer 1 blockchains, like transaction costs and scalability of transactions.
Layer 2 protocols are becoming a great layer to build applications on top of so they can take advantage of the efficiencies of these protocols.
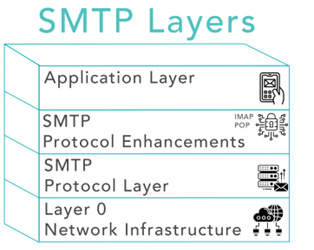
SMTP: A Familiar Parallel
(Click on image to enlarge)
If you’ve ever sent an email, you’ve used Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP), the protocol for sending and receiving emails. It operates in a similar layered fashion to blockchains.
1. Network Infrastructure: SMTP, like blockchain, relies on internet infrastructure for communication and hardware for storage.
2. Protocol Layer: SMTP is the protocol that defines how mail servers communicate. It ensures the secure and reliable transmission of email across the internet.
3. Protocol Enhancements: Extensions to SMTP, like encryption layers and additional mail protocols such as IMAP and POP, enhance the functionality and efficiency of SMTP.
4. Application Layer: This is your email client—Gmail, Outlook, Apple Mail—providing a user-friendly interface for sending and receiving emails. This allows you to send and receive emails without understanding the underlying protocols or how they work or needing to set up your own email server.
(Click on image to enlarge)
The Invisible Technology of Digital Assets
Just as you don’t need to understand SMTP to send an email, the future use cases of blockchains will likely be invisible to most users. You won’t need to know how a smart contract works to use a decentralized application any more than you need to know how your car engine works to drive to work.
As more and more services migrate to blockchains, it will start to become more common that we are using blockchain technologies.
But why should we care about understanding the nuts and bolts of these technologies if they’re going to be invisible?
The answer lies in the crypto assets that are related to those blockchains.
We haven’t had assets tied to a potentially fundamental protocol like a blockchain before. With SMTP, there wasn’t a newly formed asset class tied to the protocol. You could invest in companies building the application layer or the technology, but that was it.
In addition to tokenized real-world assets on blockchains, some crypto assets are used to reward validators or miners who keep the network secure through their consensus mechanisms. If you want to learn more about the consensus mechanisms and how they work, this is a great explanation that dives deeper into them.
Looking Forward
Understanding these fundamentals gives us a better grasp of the digital landscape and where it’s heading.
As the saying goes, “The best way to predict the future is to create it.” By understanding the fundamentals of digital assets and blockchains, we position ourselves not as passive consumers of technology but as active participants in shaping our digital future.
So the next time you send an email, use your smartphone, surf the web or make online purchases, realize there is a vast amount of technology powering our actions, and blockchains might be added to the list.
More By This Author:
Some Perspective On Banking Woes: Two Months LaterFed Watch: The Waiting Is The Hardest Part
A Strong Start For Digital Assets In 2023