Resilient US Jobs Market Backs The Case For Another 75bp Hike
The US added 263,000 jobs in September while the unemployment rate dropped back to just 3.5%. A lack of suitable workers continues to constrain the economy with job vacancies exceeding the number of unemployed Americans by more than 4mn and with core inflation set to rise further next week a 75 basis point Fed hike on 2 November is virtually assured.

Strong job creation continues
The US added 263k jobs in September with 11k of upward revisions to the past 2 months – close to the consensus of 255k. The payrolls data shows solid gains in most areas with manufacturing rising 22k despite the ISM employment index moving into contraction territory. Construction rose 19k while private service-providing firms increased payrolls by 244k. Within services, it was a little more mixed with retail (-1k), financial (-8k) and trade/transport (+3k) well down on recent months' job gains while leisure and hospitality (+83k) and education/health (+90k) look strong. Government is a drag once again, losing 25k jobs. This leaves total payrolls at 153.0mn, a new record high and half a million above the February 2020 pre-pandemic high.
US non-farm payrolls level (mn)
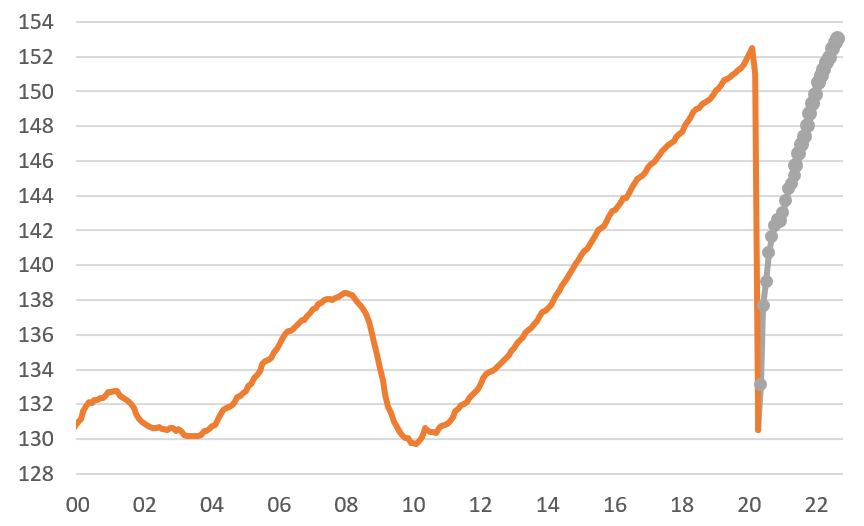
Source: Macrobond, ING
But it could have been even stronger with demand still exceeding supply
Meanwhile, the household survey shows the unemployment rate dropped back to 3.5% from 3.7% thanks to the combination of rising employment (+204k) on this survey’s calculations and people leaving the workforce (-57k). We had suspected the unemployment rate would fall given the big rise in the participation rate last month of 0.3pp to 62.4% is rarely ever held onto in the subsequent month. The 3.5% unemployment rate matches the low seen in July. The chart shows the weakness in participation is primarily due to older (55+) workers not having returned to the workforce, which suggests early retirements or possible health worries remain a major factor behind the lack of workers to fill vacant job positions.
Change in participation rate by age (percentage points since Dec 2019)
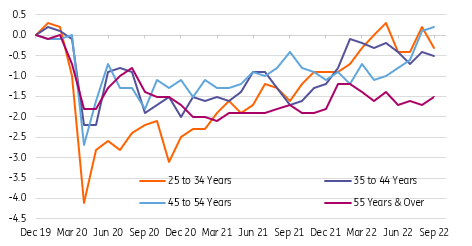
Source: Macrobond, ING
Rounding out the report, wages were in line with consensus at 5% year-on-year, down from 5.2% in August and the average work week remained at 34.5 hours.
Inflation pressures remain strong so another 75bp is on its way
The report is on the stronger side of expectations overall, with payrolls growth more constrained by a lack of suitable workers to fill positions rather than any meaningful downturn in hiring intentions – there are still 4mn more vacancies that there are unemployed Americans to fill the positions. This indicates that the Fed has more work to do to slow the economy in order to get inflation under control. In this regard note next week’s core CPI inflation rate (published 13 October) is expected to RISE to 6.5% from 6.3% next week. We were down at “only” 5.9% in June and July and this unfavourable shift when the labour market remains so tight means that a 75bp hike at the 2 November Federal Open Market Committee meeting remains the obvious call.
More By This Author:
The Commodities Feed: Oil Moves HigherCopper: All Eyes Are On China
US: A Cold Wind Is Blowing
Disclaimer: This publication has been prepared by the Economic and Financial Analysis Division of ING Bank N.V. (“ING”) solely for information purposes without regard to any ...
more


