Economics For Everyone- Gearing Up For G20
Overview
The G20 (Group of 20) is an international forum for the governments and central bank governors from 19 countries and the European Union (EU). It is formally known as the 'Summit on Financial Markets and the World Economy.' The main purpose of G20 was to bring together systematically important industrialized and developing economies to discuss key issues in the global economy.
The recent editions of G20 not only focus on macro economy and trade but also focus on global issues that directly or indirectly impact the global economy. Some of the examples include climate change, health, migration, terrorism, water crises, etc.
The key objectives of G20 are-
- Policy coordination between its members to achieve global economic stability and sustainable growth.
- To promote financial regulations that reduce risks and prevent future financial crises.
- To create a new international financial architecture.
Background
In September 1999, the finance ministers and central bank governors of the Group of Seven countries (the G-7) announced their intention to “broaden the dialogue on key economic and financial policy issues among systemically significant economies and promote co-operation to achieve stable and sustainable world economic growth that benefits all.” This announcement marked the official birth of what subsequently became known as the Group of Twenty countries (the G-20). But the evolvement of G20 was quite revealing. In 1997, Russia officially joined the group and thus G7 became G8. In December 1999, a set grouping of 20 was established consisting of the G8 along with the key regional powers plus the European Union (Smith, 2011). Since 2008 G20 has expanded its agenda and heads of government or heads of state, as well as finance ministers and foreign ministers have periodically conferred at summits ever since. With the G20 growing stature after its inaugural leaders’ summit in 2008, its leaders announced on 25 September 2009 that the group would replace the G8 as the main economic council of wealthy nations.
Participating Countries
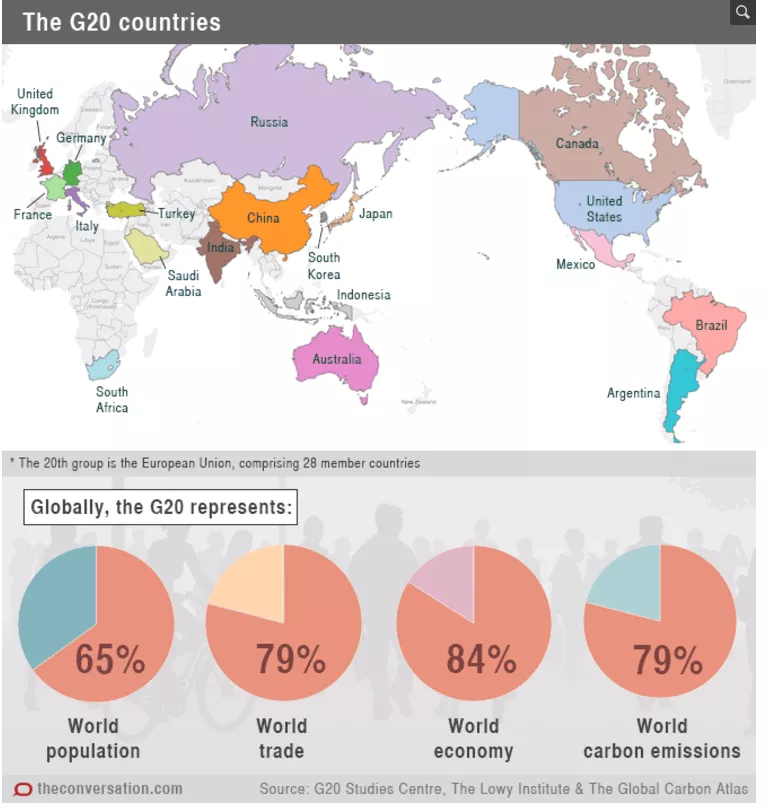
Membership of the G20 consists of 19 individual countries plus the European Union. The participating countries are- Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, European Union, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, South Korea, Turkey, United Kingdom, United States.
Why does G20 matter?
G20 economies account for around 80% of the Gross World Product (GWP), 75% of the world trade, two-thirds of the world population, and approximately half of the world's land area. These figures have remained relatively stable while the corresponding rates for Group of Seven (G7) nations, a smaller group of advanced democracies, have shrunk, as emerging markets take up a relatively greater share of the world’s economy.
Importance of G20 Summit
1. Economic stability: The G20 summit brings together the world's largest economies and financial powers to discuss and coordinate economic policies that can help stabilize the global market.
2. Climate change: With the increasing threat of climate change on the world's economies, the G20 summit can provide a platform for nations to work together towards finding sustainable solutions that reduce carbon emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
3. Trade agreements: The G20 summit is an opportunity to negotiate and establish new trade agreements, which can help boost global trade and improve economic conditions for all nations involved.
4. Social welfare: The G20 summit can address global issues related to poverty, inequality, and lack of access to basic services. This includes discussing policies and initiatives that can improve social welfare, such as health care, education, and social security.
5. Political stability: The G20 summit can help promote political stability and cooperation between nations by discussing issues related to terrorism, political unrest, and human rights violations. This can help create a more peaceful and stable global environment.
6. Global Recovery from COVID-19: The G20 summit can be instrumental in coordinating global efforts to recover from the COVID-19 pandemic. This includes discussing vaccine distribution, economic stimulus packages, and public health measures.
7. Innovation and Technological Advancement: The G20 summit can provide a platform to discuss and promote innovation and technological advancement across nations. This can help encourage collaboration and investment in areas such as artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and digitalization.
8. International Cooperation: The G20 summit can foster international cooperation by bringing together leaders from different nations and regions. This can help promote dialogue, understanding, and collaboration, even in the face of political and social differences.
9. Sustainable Development: The G20 summit can prioritize sustainable development by discussing and implementing policies that promote environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and economic growth. This can help ensure a better future for current and future generations.
10. Financial Regulation: The G20 summit can address financial regulation by promoting transparency, accountability, and oversight in the global financial system. This includes discussing policies and regulations that can prevent financial crises and promote stable economic growth.
In one of the earlier G20 Summits Prime Minister Narendra Modi held wide-ranging talks with US President Donald Trump and discussed ways to leverage the power of technology, improve defence and security ties as well as issues relating to trade, Iran, and 5G. The two leaders discussed Iran, 5G, bilateral relations, and defense ties on the sidelines of the summit. The US reimposed sanctions on Iran in November after pulling out of a 2015 nuclear accord between Tehran and six world powers. To reduce Iran's crude oil export to zero, the US ended on May 2 waivers that had allowed the top buyers of Iranian oil, including India, to continue their imports for six months. India, complying with the US sanctions, has ended all imports of oil from Iran.
India holds the Presidency of the G20 from 1 December 2022 to 30 November 2023.

Importance of G20 Summit
1. Economic stability: The G20 summit brings together the world's largest economies and financial powers to discuss and coordinate economic policies that can help stabilize the global market.
2. Climate change: With the increasing threat of climate change on the world's economies, the G20 summit can provide a platform for nations to work together towards finding sustainable solutions that reduce carbon emissions and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
3. Trade agreements: The G20 summit is an opportunity to negotiate and establish new trade agreements, which can help boost global trade and improve economic conditions for all nations involved.
4. Social welfare: The G20 summit can address global issues related to poverty, inequality, and lack of access to basic services. This includes discussing policies and initiatives that can improve social welfare, such as health care, education, and social security.
5. Political stability: The G20 summit can help promote political stability and cooperation between nations by discussing issues related to terrorism, political unrest, and human rights violations. This can help create a more peaceful and stable global environment.
6. Global Recovery from COVID-19: The G20 summit can be instrumental in coordinating global efforts to recover from the COVID-19 pandemic. This includes discussing vaccine distribution, economic stimulus packages, and public health measures.
7. Innovation and Technological Advancement: The G20 summit can provide a platform to discuss and promote innovation and technological advancement across nations. This can help encourage collaboration and investment in areas such as artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and digitalization.
8. International Cooperation: The G20 summit can foster international cooperation by bringing together leaders from different nations and regions. This can help promote dialogue, understanding, and collaboration, even in the face of political and social differences.
9. Sustainable Development: The G20 summit can prioritize sustainable development by discussing and implementing policies that promote environmental sustainability, social responsibility, and economic growth. This can help ensure a better future for current and future generations.
10. Financial Regulation: The G20 summit can address financial regulation by promoting transparency, accountability, and oversight in the global financial system. This includes discussing policies and regulations that can prevent financial crises and promote stable economic growth.
In one of the earlier G20 Summits Prime Minister Narendra Modi held wide-ranging talks with US President Donald Trump and discussed ways to leverage the power of technology, improve defence and security ties as well as issues relating to trade, Iran, and 5G. The two leaders discussed Iran, 5G, bilateral relations, and defense ties on the sidelines of the summit. The US reimposed sanctions on Iran in November after pulling out of a 2015 nuclear accord between Tehran and six world powers. To reduce Iran's crude oil export to zero, the US ended on May 2 waivers that had allowed the top buyers of Iranian oil, including India, to continue their imports for six months. India, complying with the US sanctions, has ended all imports of oil from Iran.
India holds the Presidency of the G20 from 1 December 2022 to 30 November 2023.
More By This Author:
Economics For Everyone - Gains Of Green RevolutionEconomics For Everyone: The Insolvency And Bankruptcy Code In India And The National Company Law Tribunal
Economics For Everyone – Walls Of The World
Disclosure: None



