August 2014 CPI Inflation Moderates, Well Under Expectations
The August 2014 Consumer Price Index (CPI-U) year-over-year inflation rate moderated. Energy prices decreased significantly whilst food increased moderately. The annual core inflation rate declined and is under the targets set by the Federal Reserve.

The Consumer Price Index (CPI-U) year-over-year inflation rate declined from 2.0% to 1.7%. Year-over-Year core inflation (CPI less food and energy) also declined from 1.9% to 1.7%. The market expected:
| month over month change | Consensus Range | Consensus | Actual |
| CPI-U | -0.1 % to 0.1 % | 0.0% | -0.2% |
| CPI-U less food and energy | 0.0 % to 0.2 % | 0.2% | 0.0% |
Unadjusted CPI-U - Year-over-Year Change (blue line, left axis) and Month-over-Month Change (red line, right axis)
The Producer Price Index annual rate of inflation showed finished goods rose slightly 0.1% to 1.8% in August 2014. The CPI rate of inflation is normally higher than the PPI - but not so this month.
As a generalization – inflation accelerates as the economy heats up, while inflation rate falling could be an indicator that the economy is cooling. However, inflation does not correlate well to the economy – and cannot be used as a economic indicator.
Energy commodities by far was the major influence on this month’s CPI.
The Consumer Price Index for All Urban Consumers (CPI-U) decreased 0.2 percent in August on a seasonally adjusted basis, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today. Over the last 12 months, the all items index increased 1.7 percent before seasonal adjustment.
The seasonally adjusted decline in the all items index was the first since April 2013. The indexes for food and shelter rose, but the increases were more than offset by declines in energy indexes, especially gasoline. The energy index fell 2.6 percent, with the gasoline index declining 4.1 percent and the indexes for natural gas and fuel oil also decreasing.
The index for all items less food and energy was unchanged in August; this was the first month since October 2010 that the index did not increase. While the shelter index increased and the indexes for new vehicles and for alcoholic beverages also rose, these advances were offset by declines in several indexes, including airline fares, recreation, household furnishings and operations, apparel, and used cars and trucks.
The all items index increased 1.7 percent over the last 12 months, a decline from the 2.0 percent figure for the 12 months ending July, and the smallest 12-month change since March. The index for all items less food and energy also rose 1.7 percent over the last 12 months. The food index has risen 2.7 percent over the span, while the energy index has increased 0.4 percent.
Historically, the CPI-U general index tends to correlate over time with the CPI-U’s food index. The current situation is putting an upward pressure on the CPI.
CPI-U Index compared to the Food sub-Index of CPI-U

Notice the gap in the above graphic between the CPI and Food – historically this gap has always closed when the knock-on effect from higher food prices into other CPI components moderates.
The Federal Reserve has argued that energy inflation automatically slows the economy without having to intervene with its monetary policy tools. This is the primary reason the Fed wants to exclude energy from analysis of consumer price increases (the inflation rate).

In the above chart – the green boxes are significant elements moderating inflation, while the red boxed items are significant elements fueling inflation.
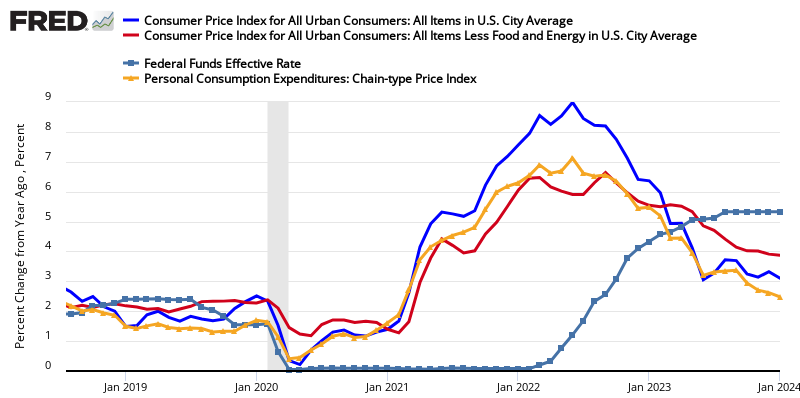
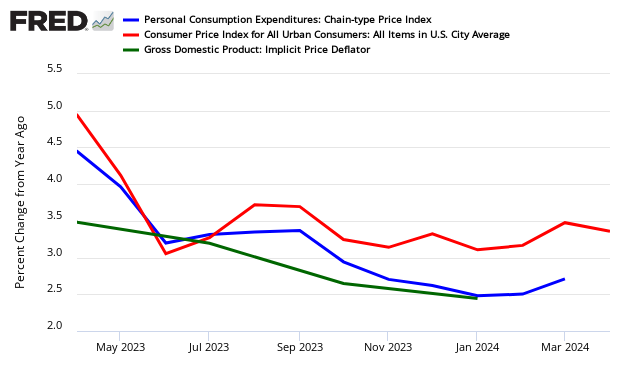
The graph below looks at the different price changes seen by the BEA in this PCE release versus the BEA’s GDP and BLS’ Consumer Price Index (CPI).
Year-over-Year Change – PCE’s Price Index (blue line) versus CPI-U (red line) versus GDP Deflator (green line)
Detailed Analysis
The first chart is an overlay of Headline CPI and Core CPI (the latter excludes Food and Energy) since the turn of the century. I've highlighted 2 to 2.5 percent range, which the Federal Reserve currently targets for the CPI's cousin index, the BEA's Personal Consumptions Expenditures (PCE) price index.

The next chart shows both series since 1957, which was the first time the government began tracking the core inflation metric.

In the wake of the Great Recession, two percent has been the Fed's target for core inflation. However, at their December 2012 FOMC meeting, the inflation ceiling was raised to 2.5% while their accommodative measures (low Fed Funds Rate and quantitative easing) are in place.
Federal Reserve policy, which has historically focused on core inflation, and especially the core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE), remains slightly below the target range of 2 to 2.5 percent.
Caveats on the Use of the Consumer Price Index
Econintersect has performed several tests on this series and finds it fairly representative of price changes (inflation). However, the headline rate is an average – and will not correspond to the price changes seen by any specific person or on a particular subject.
Although the CPI represents the costs of some mythical person. Each of us need to provide a multiplier to the BLS numbers to make this index representative of our individual situation. This mythical person envisioned spending pattern would be approximately:

The average Joe Sixpack budgets to spend his entire paycheck or retirement income – so even small changes have a large impact to a budget.
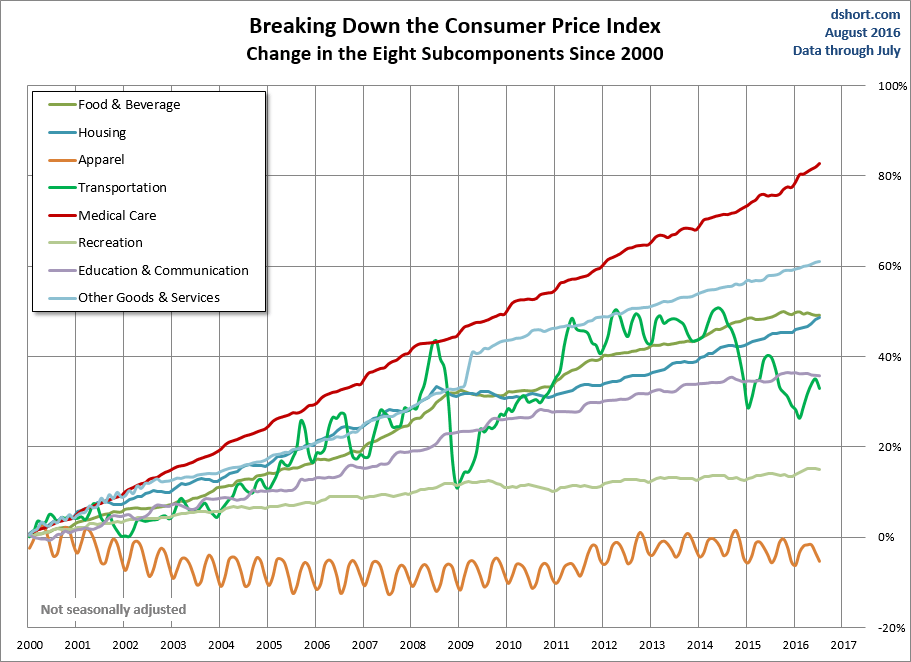
The graph above demonstrates that fuel costs, medical care, and school costs are increasing at a much faster pace than the headline CPI-U.
The Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) has compiled CPI data since 1913, and numbers are conveniently available from the FRED repository (here). Long-term inflation charts reach back to 1872 by adding Warren and Pearson’s price index for the earlier years. The spliced series is available at Yale Professor (and Nobel laureate) Robert Shiller’s website. This look further back into the past dramatically illustrates the extreme oscillation between inflation and deflation during the first 70 years of our timeline. Click here for additional perspectives on inflation and the shrinking value of the dollar.

The chart below includes an alternate look at inflation*without* the calculation modifications the 1980s and 1990s (Data from www.shadowstats.com).

Because of the nuances in determining the month-over-month index values, the year-over-year or annual change in the Consumer Price Index is preferred for comparisons.
Disclosure: None.



