Futures Options
Chances are you may know about options. Perhaps you have also heard of futures. But have you heard of futures options? Futures options can sometimes provide the best of both worlds for traders on certain products.
This article will break down what futures options are. We will then explore some of the benefits and when to use them in a portfolio.
What are Futures Options?
A futures option is an option on a futures contract that gives the holder the right to buy or sell a given asset at a specific price for a certain period of time. If this sounds similar to an options contract, it is because they are almost the same.
A futures call option, for example, will have the same exposures to greeks that a call option on a stock would have. Thus, if you have experience with options, branching into futures options isn’t difficult. The major difference is that the underlying in this case is not a stock or an ETF, it is a futures contract itself.
What are the Benefits of Future Options?
-
They are More Margin-Efficient
The biggest benefit to trading futures options is access to greater leverage through the SPAN Margin. This allows options sellers to trade with substantially more size than what is available from selling options on stocks, as this uses the Reg T margin. Below is an example of the margin requirement for selling one at-the-money futures options put on an ES contact.
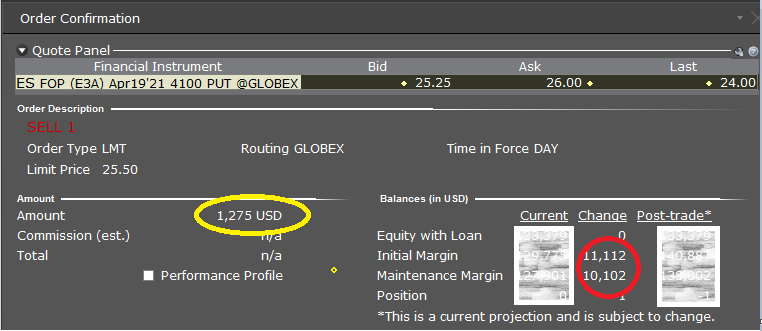
We can see that by selling this ES put, we receive a credit of $1,275 (in yellow) and have to provide $11,112 in Initial Margin (in red). Now let’s compare that to selling 5 SPY puts, which is the same notional value as our one ES futures option.
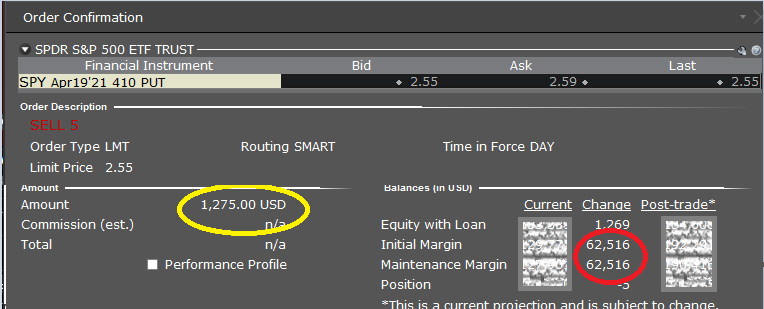
Here we have the same credit and the same exposures. We are selling the same notional value on the S&P 500. Despite this, we have a shocking $62,516 margin we have to provide. This is all because of the SPAN vs. REG-T calculation, not due to real risk. In this case, the superior margin efficiency under the SPAN margin makes selling the ES option a much better bet.
-
Futures Options are Superior for Commodity and Currency Volatility.
For trading volatility on currencies and commodities outside of gold, silver, and oil, it is almost necessary to trade the futures options. This is because the ETFs tracking these products are few and illiquid.
For example, if a trader wanted to trade soybeans, the largest ETF, SOYB, has only a hundred million dollars of assets under management and relatively illiquid options. This makes it difficult to trade. In contrast, Soybean futures and futures options are liquid, margin-efficient, and allow investors to get the exact exposures they want.
Does this make Futures Options more Profitable than Options?
The simple answer is: no. It only allows traders to apply more leverage. When you have two trades with a positive expected value, applying more leverage will increase profitability. If you have no advantage in your trade, adding leverage doesn’t add profitability. If anything, you will just end up losing money faster.
How are Futures Options Settled?
One of the most confusing things about futures options is settlement. Regular options on stocks and ETFs will involve settlement by purchasing or receiving the specified number of shares if the contract ends in-the-money. For equity futures, options settlement is normally to the underlying futures contract or simply to cash, as demonstrated by the ES settlement details below.
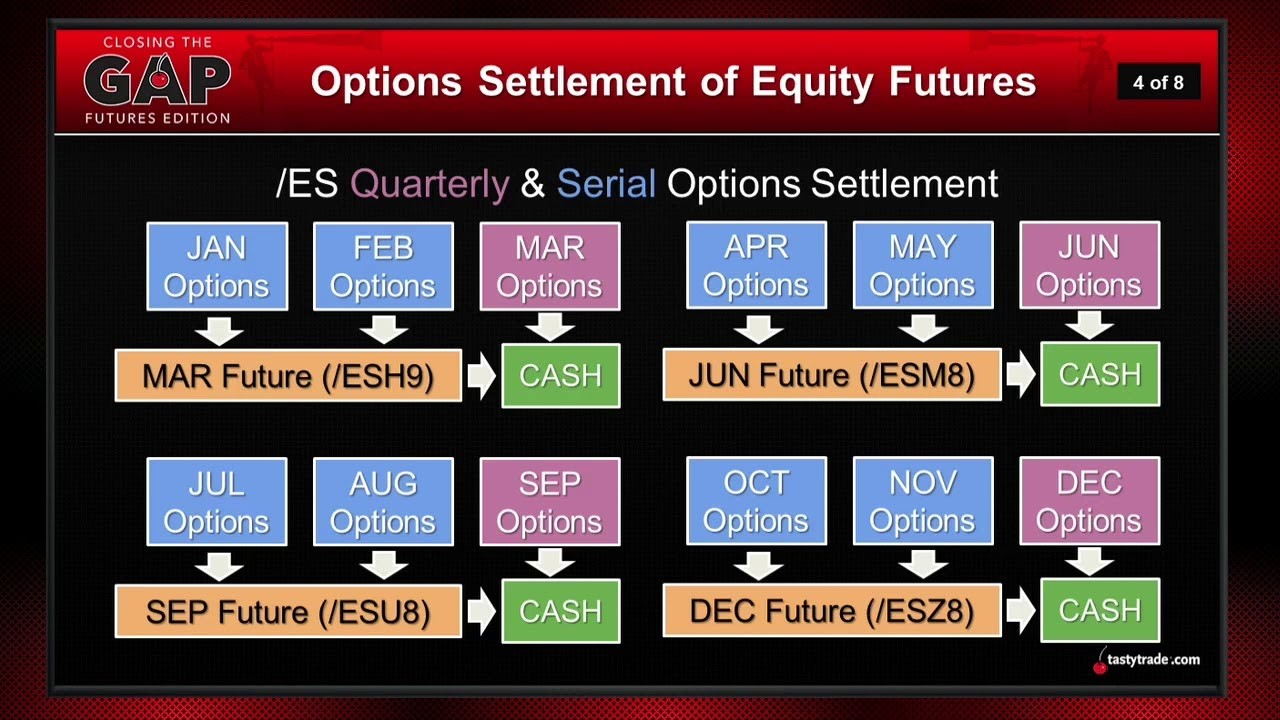
Source: Tastytrade
We can see here that the options for all the major quarterly expirations settle to cash, while other expires settle to the upcoming futures contract. In the event that the futures option is settled to cash, there is no further action needed. If it is settled to the underlying future, one simply buys or sells the future position on assignment or closes the options position before assignment to the future.
In contrast, most commodity and currency futures require physical delivery. If you are reading this article, chances are you do not have the capacity nor permissions to store 1,000 barrels of oil in your backyard. Thus, you will be forced to close out a position before settlement and delivery.
If you wish to maintain exposure, one can simply establish a new options position in the next futures cycle. If you forget to close out the position after a few reminders from the brokerage, your position will be liquidated. This usually isn’t the end of the world as liquidity is generally good.
Should I Trade the Futures or Futures Options?
In order to decide whether to trade futures or futures options it is important to establish your view on the asset you want to trade. As a speculator, if you do not have a view on the volatility of the instrument you are trading, it is almost always better to trade the underlying. This holds true for stocks vs. options.
The same applies for futures and futures options. The reality is the futures contract will always be more liquid than the futures options. When a trader purchases or sells future options, they introduce all the greeks into the equation.
As an example, imagine John is bullish on the price of oil. The May Crude oil contract is trading at $60, so he buys the $80 call for $1.50. John is right on direction and the price of crude goes up, and by the time the contract expires, crude is trading at $78. John lost all his money. He was right on direction but wrong on volatility (a view he didn’t have), and his call expires worthless.
If he had simply bought the underlying future, he would have made $18. On the other side, as a hedger, an investor again has to decide how much risk they want to hedge off.
Airlines, for example, commonly buy OTM calls on oil to hedge their risks. The reason being that small fluctuations in the price of oil will not bring down an airline or cause major reductions in consumer demand. Yet if the price of oil triples in a few months, that spells trouble.
Using futures options allows them to hedge against risk they are unwilling to take in an effective manner. Take the risks you want to have, hedge against all others.
Concluding Remarks
Futures options allow investors access to options on a vast array of futures products. It allows enhanced leverage and hedgers to specifically hedge risks on their book. For investors already familiar with options trading, futures options can offer a perfect vehicle for trading the volatility of equity indices, commodities, and currencies.



