Expect The Eurozone Labor Market To Remain Tight Despite Recession
This report finds that tight labor markets ahead of a recession cause employment to fall less than normal. So, given that we expect a shallow recession in the eurozone, labor shortages are not going to disappear in all countries and sectors, and modest upward pressure on wages is set to stay.
The European Commission has joined the long list of organizations now expecting a recession to happen in the eurozone this winter. Only a few optimists seem to be holding out and expect the economy to avoid recession altogether. To us, the evidence is adding up to a modest recession with two quarters of negative growth and a very shallow recovery.
From an unemployment perspective, most seem to expect that the impact will be relatively small given that labor markets are currently exceptionally tight. Despite that, we do see hiring intentions falling, and some countries have noticed small increases in unemployment already. So the question to answer is, does a tight labor market at the start of a recession actually matter for the employment outcome during the recession? We think it does; here's why.
Expect unemployment to increase as recession starts
As an economy enters recession, we see an increase in unemployment. When looking back at the six previous eurozone recessions since the 1970s, we find that this has been the case. As you can see in the chart below, the increase in unemployment generally starts when the recession begins but drags on much longer.
2020 is the exception as furlough schemes and an exceptionally quick recovery resulted in a break with the trend, three quarters after the start of the recession.
Unemployment increases in times of recession
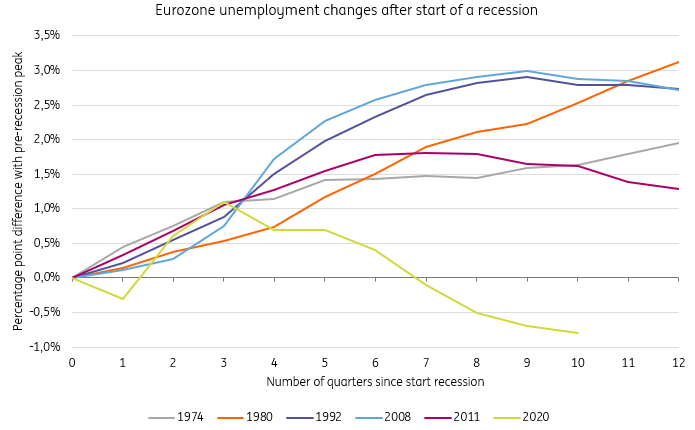
Source: Eurostat, The Area Wide Model, ING Research
The furlough scheme safety net seems unlikely to be used to the extent it was during the pandemic as governments reign in support and because the nature of the downturn is different. Also, labor markets are already exceptionally tight at the moment, which means that a certain amount of labor turnover will be welcomed as a relief to some. Without a government response, but with very tight labor markets at the start of this downturn, the question is whether companies will engage in labor hoarding; keeping people on the payroll to make sure that they have good workers available when the downturn ends because it’s so hard to find workers in this economy.
In times of labor shortages, recessions have a smaller labor market impact
A marginal labor market impact of the upcoming recession seems to be the consensus view, also iterated by the European Commission in its autumn forecast: “The unemployment rate is thus projected to increase only marginally from a historic low”. We take some comfort from past episodes regarding this call. Analyzing downturns by country and sector in the eurozone since 2006, we find that high labor shortages at the start of a downturn resulted in a smaller negative impact on employment.
This finding is statistically significant, indicating that in general, we can expect a weaker decline in employment because we now see current high labor shortages. As the two charts below indicate, we find a flatter relationship between GDP and employment in downturns that were preceded by high vacancy rates (so high labor shortages). So it looks like businesses indeed engage in labor hoarding in times of very tight labor markets.
The employment response to a decline in output is smaller when labor shortages are high
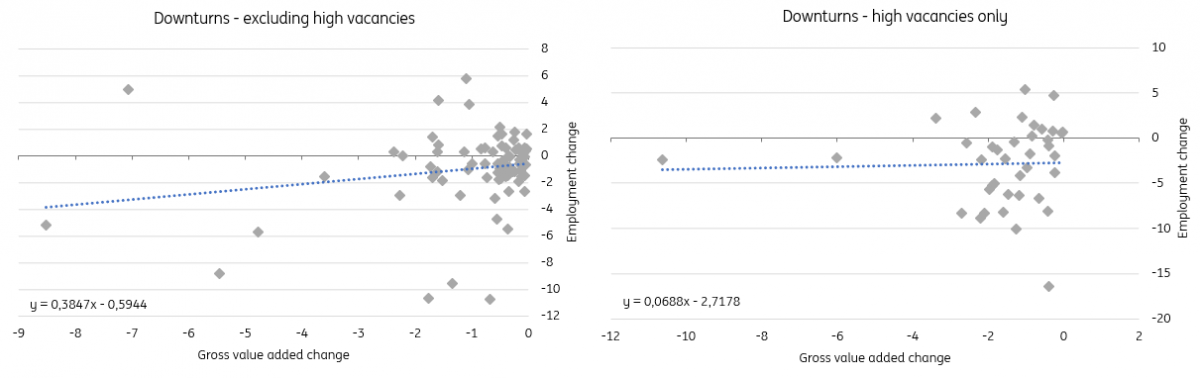
Source: Eurostat, ING Research calculations
To arrive at this conclusion, we use quarterly vacancy rates, gross value-added, and employment data by eurozone country and sector, which gives us a large dataset in which ample downturns occur. We identify periods of high labor shortages as vacancy rates that are in the highest 10% of vacancy rates across sectors and countries at that time. For downturns, we use periods of at least two quarters of consecutive declines in gross value added.
The employment response is one that we measure both coincidentally and with four quarters of lags. We stopped the sample of data used in the fourth quarter of 2019 because of the impact of furlough schemes, which likely distorted the relationship. We have tried slightly different models, of which most show a statistically significant impact of high vacancy rates on employment.
Results from our panel data regression show that employment behaves differently in recessions when vacancy rates are high
Labor shortages are therefore unlikely to disappear despite an expected recession
Taking the previous exercise into account, this means that a modest increase in unemployment is to be expected given the already mild recession that we forecast for the eurozone over the course of the winter months. While that is set to cool the labor market somewhat, the question is whether this will be enough for shortages to disappear. That seems doubtful at this point. The unemployment rate fell to a new historic low of 6.5% in October despite the economy slowing quite dramatically. It looks like the countries and sectors with particularly hot labor markets could remain tight despite the economy contracting over the winter and experiencing just a mild recovery.
Don’t forget that demographics also weigh more and more on potential labor supply, which means that shortages are set to become more structural anyway. The fact that the upcoming recession is unlikely to cool the market much means that structural shortages will likely be quite visible over the coming years.
With unemployment at record lows now, shortages are set to become more structural
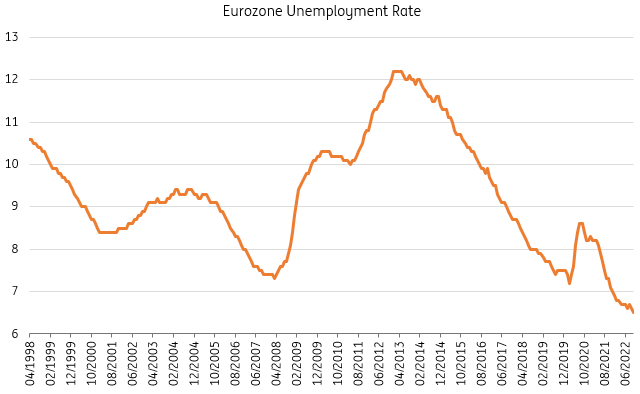
Source: Eurostat, ING Research
More By This Author:
FX Daily: Easing Into Year-EndAsia Morning Bites Mon, Dec 19
Asia Week Ahead: Potential Rate Hike From Bank Indonesia
Disclaimer: This publication has been prepared by ING solely for information purposes irrespective of a particular user's means, financial situation or investment objectives. The information ...
more



