The 1% And The Bond Market
With the bond market confounding forecasters and prognosticators once again, I thought I delve into one of the more mysterious reasons why the bond market keeps going from strength to strength.
To a man, hedge fund traders expected bond prices to take a dive in 2014 and 2015, and for yields to soar. Isn’t that what’s supposed to happen in recovering economies?
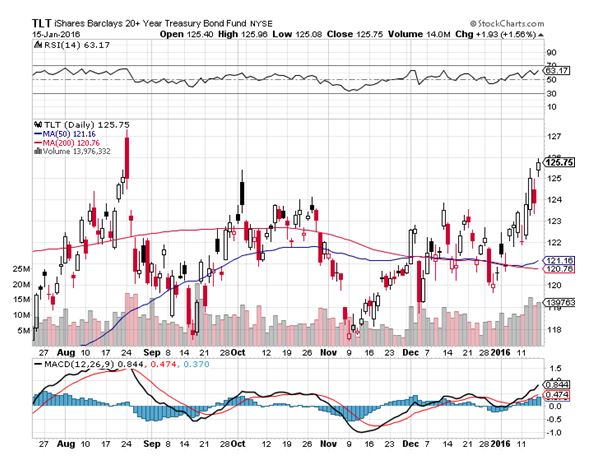
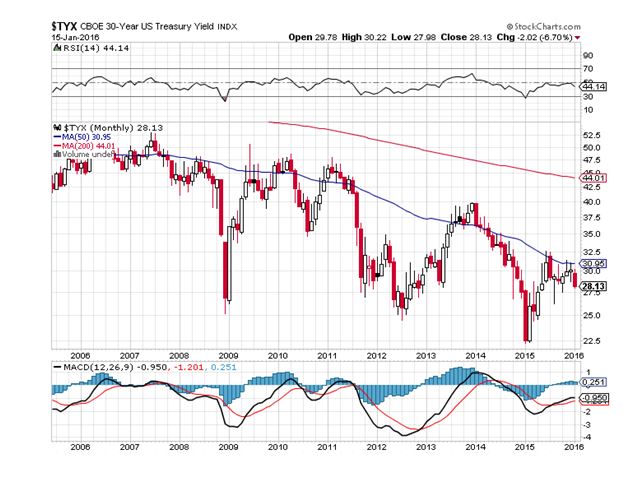
Instead, we got the opposite, and yields have plunged, from 3.05% for the ten-year Treasury to as low as 2.80% this week.
There are many important lessons to be learned here. This is not your father’s bond market.
The internal dynamics of the fixed income markets have changed so much in the last three decades that it has become unrecognizable to long term practitioners, like myself.
A big factor has been the takeover of the bond market by the 1%, the richest segment of the US population, and indeed, the global economy. As wealth concentrates at the top, its character changes.
Let me stop here and tell you that the ultra rich are different from you and I, and not just because they have more money.
I have learned this after nearly half century long relationships with the planet’s wealthiest families, including the Rockefeller’s, Rothschild’s, DuPont’s, Morgan’s, and Pritzkers, first as important contacts of mine at The Economist magazine, then as clients of mine at Morgan Stanley, then as investors in my hedge fund, and now as readers of The Diary of a Mad Hedge Fund Trader.
The wealthier families become, the more conservative the get in their investment choices. Their goal shifts from capital appreciation to asset protection.
They lose interest in return on capital and become obsessed with return of capital. This is how the rich stay rich, sometimes for centuries. I have even noticed this among my newly minted billionaire hedge fund buddies.
What this means for the bond market is that they never sell. When they buy a 30-year Treasury bond, it is with the expectation of keeping it for the full 30 years, until it matures.
That way they can avoid capital gains taxes and only have to pay interest on the coupon payments. When they die, spouses get the step up in the cost basis, and then the wealth passes from one generation to the next. Taxes are never paid.
Back in the 1980’s, when wealth was more evenly distributed, the top 1% only accounted for 1% of Treasury bond ownership. Today, that figure is closer to 25%.
Add this to the 50% of our national debt that is owned by foreign investors, who also tend to also hold paper for its full life. Central banks don’t pay taxes either.
China and Japan, and the biggest holders, with around $1 trillion each. This means that 75% or more of Treasury bonds are owned by investors who won’t sell. What does that mean for the rest of us? Bond prices that never go down.
With bonds very close to 30-year highs, keeping these securities have been the right thing to do. I can’t tell you how many investment advisors I know who have distilled their practices down to fixed income instruments only.
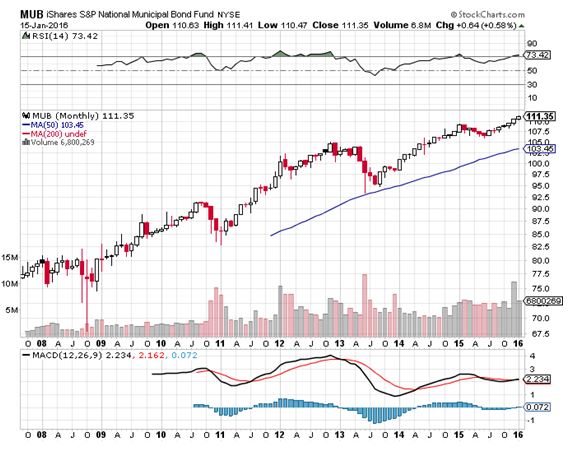
This involves the entire coupon clipping space, including municipal bonds (MUB), corporates (LQD), junk (JNK), and even emerging market debt (ELD).
This is driven by customer demand, the 1% er’s, not from any great insights or epiphanies that they achieved on their own.
Of course, there is a certain amount of driving with your eyes firmly fixed on the rear view mirror going on here. Maybe the rich will finally sell their bonds once prices fall hard, stay down, and then go down some more.
Inflation rearing its ugly head might also do the trick, which is always bad for bond prices, as it reduces the purchasing power of money. Selling is certainly what they were doing with both hands in the early eighties, when the ten-year yield hit 12%.
Again, the rear view mirror effect kicked in big time, when bonds were called “certificates of wealth confiscation.”
There are other maters to consider with the 1% owning so much of the bond market and keeping it there.
This is money that is not getting invested in new start up and creating jobs. It is money that is not being used to engender new economic growth. One of the fantasies of the last election was the claim that the 1% were creating so many jobs. They weren’t, not as long as their money was parked in a risk free bond market.
Instead, it is just stagnating. This is one reason why economic growth is so flaccid this decade, and will remain so. This is fine for the 1%, but not so good for the rest of us.
The bottom line here is that while bonds are overbought and due for a pullback, they are not by any means going to crash. We could be living in the 2.60%-3.50% range for the 30-year for quite some time, maybe for years.
That is if the new Federal Reserve governor and my friend, ultra dove, Janet Yellen, has anything to say about it. She has only just started and could be with us for another eight years.
Personally, I don’t foresee any appreciable rise in interest rates until we get well into the 2020’s, when real inflation finally returns from the dead.
That is when bonds will become the asset class you don’t want to know, whether you’re in the 1% or not.
Disclosure: None.




Nice article. Fascinating, in fact. This adds to my claim that bonds are in massive demand for collateral. People are desperate to buy them, and if the rich aren't selling them, it just makes demand all the more intense. Thanks, John.
It also argues against the Fed pushing too much money to the top all the time.