R-Word Index, Google Trends And Gold
Everyone is discussing recession right now. But how much do they actually chatter about it? Does this talk reflect or change people's perception? And the key question is: can the world-related indices predict the recession? Are they useful for the precious metals investors?
It turns out that yes! At least to some extent. Let's start with the R-word index created by The Economist. It counts how many stories in The Washington Post and The New York Times are using the word "recession" in a quarter. The idea behind the indicator is that economic downturn coincides with a surge in the frequency of the that scary world starting with R. The index surges when recessions are on the minds of people and the financial journalists who write articles about them. And, indeed, it has been pretty good at spotting economic turning points over the past three decades. As one sees in the figure below, the R-word index signaled the start of recessions in America in 1990, 2001, and 2007.
Chart 1: The Economist's R-word Index from Q1 1990 to Q4 2018.
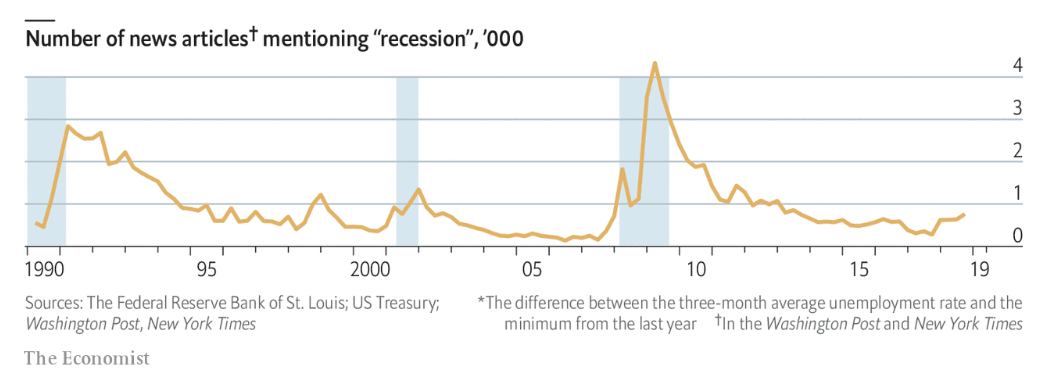
Is it a perfect indicator? Of course not! The R-word index is great because it is instantly available. However, it emits a recessionary signal just before the crises, so it is not the best leading indicator. And it sent a false warning in 1998. Moreover, the size of the spike in the early 1990s was much higher than during the previous recessions, although they were much more severe.
Another problem is that the gauge sometimes indicates recessions after they officially end, as the journalists go on babbling about the slump even when it's over. This is the main limitation of the index: it does not measure the real economic activity but its perception in just two newspapers (however, Mark Doms and Norman Morin, in a paper "Consumer Sentiment, the Economy, and the News Media", elaborated of The Economist's R-word index, constructing indexes reflecting the number of articles about recession from 30 large newspapers, and they reached similar conclusions). If these two match each other, that's perfect. But the perception can be distorted. Remember that the press loves to shock, as fear sells great.
Currently, the index is not flashing danger. However, the measure is on the rise. When the number surpasses 1,000, you might start to worry, having in mind all its shortcomings. You could then consider buying gold and sit comfortably in a chair. And admire the glow of bullion, instead of counting words in the newspaper.
We all know that the media cannot be trusted, right? So maybe instead of relying on financial journalists, we should simply ask Uncle Google? After all, instead of going to the doctor, you ask the Uncle how serious your symptoms are. Google is the dominant search engine, so its search term usage can provide a snapshot of current interests in economic issues, including recession. The idea is simple: if many people are entering the same economic search terms in the same period, this could reflect changing conditions, such as the onset of a recession.
So, let's look at the chart below, which shows the gold prices and the popularity of a query for "recession" in the United States from January 2004 to June 2019.
Chart 2: Searches in Google for "Recession" in the US from January 2004 to June 2019 (January 2008 = 100).
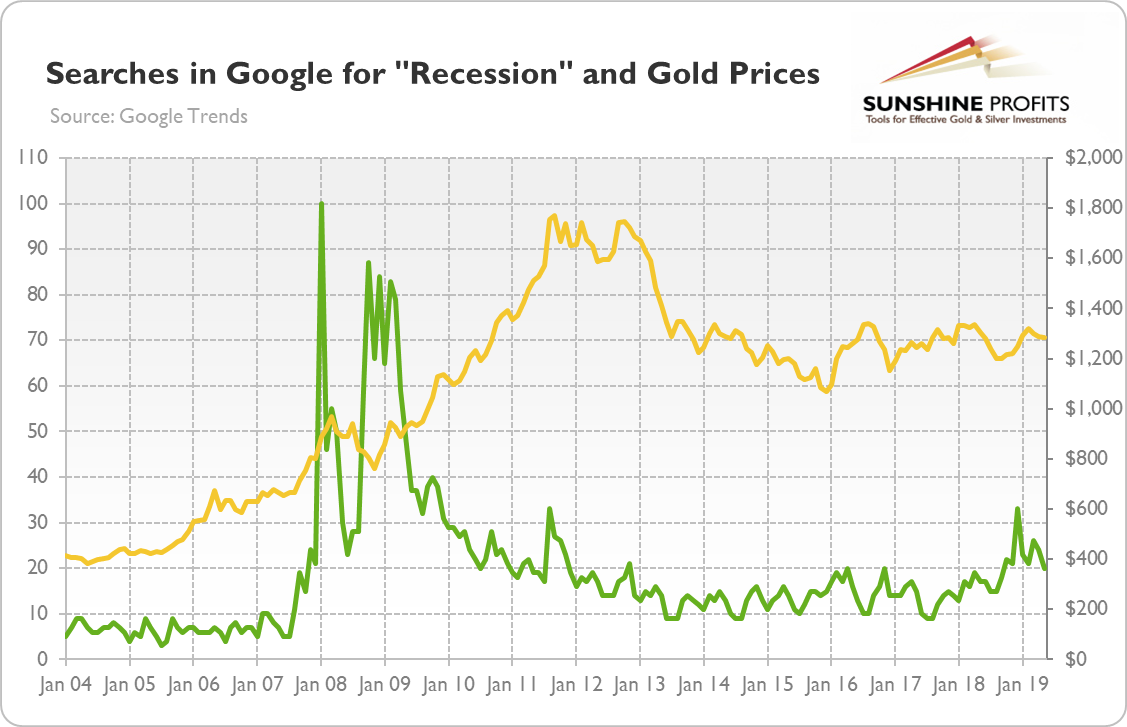
As one can see, the term gained the maximum popularity in January 2008, shortly after the official start of the Great Recession. Since then, the popularity receded but soared again after the collapse of the Lehman Brothers. Until recently, the index remained at a low level, but it surged the end of 2018. Currently (as of mid-June), it stays at 20, a level seen just before the last financial crisis. However, it has been in a downward trend in 2019, so although the jump from the end of the previous year is disturbing, there is no reason to panic yet. This indicator does not suggest an imminent U.S. recession.
However, although the index is timely, investors should remember its limitations. First of all, Google Trends data are available only from January 2004, so it covers only one economic crisis. Second, the spike in searches for "recession" occurred just when the US economy fell officially into recession, so it is not the best leading indicator.
What does it all mean for the gold market? Well, both The Economist's R-word Index and Google's Recession Index have increased substantially from their through in mid-2017, which is worrisome and could spur some safe-haven demand for gold. However, both indices do not flash recessionary signals yet. Gold bulls will have to wait to unfold fully their wings, pardon, hooves.
If you enjoyed the above analysis and would you like to know more about the most important macroeconomic factors influencing the U.S. dollar value and the price of gold, we invite you to read the ...
more


