Q2018 (Final): Headline Productivity Improving At A Faster Rate Than Labor Costs
A simple summary of the headlines for this release is that productivity improved while the labor costs slowed. Year-over-year analysis shows productivity rising faster than labor costs.

Analyst Opinion of Productivity and Costs
I only look at year-over-year data - the headline compounding distorts the view. I have issues with the way productivity is determined - see the end of this analysis.
Productivity trend is improving while unit labor cost trend is slowing.
The headlines annualize quarterly results (Econintersect uses year-over-year change in our analysis). If data is analyzed in year-over-year fashion, non-farm business productivity improved 1.3 % year-over-year, and unit labor costs were up 0.9 % year-over-year [preliminary published 1.5%]. Bottom line: the year-over-year data is saying that productivity improvements are outpacing labor cost growth.
The market was expecting:
| seasonally adjusted quarter-over-quarter at annual rate | Consensus Range | Consensus | Preliminary Actual | Final Actual |
| Nonfarm productivity | 2.2 % to 2.8 % | +2.3 % | +2.2 % | +2.3 % |
| Unit labor costs | 0.8 % to 1.2 % | +1.1 % | +1.2 % | +0.9 % |
Please note that the following graphs are for a sub-group of the report nonfarm > business.
Seasonally Adjusted Year-over-Year Change in Output of Business Sector

Seasonally Adjusted Year-over-Year Change of Output per Hour for the Business Sector
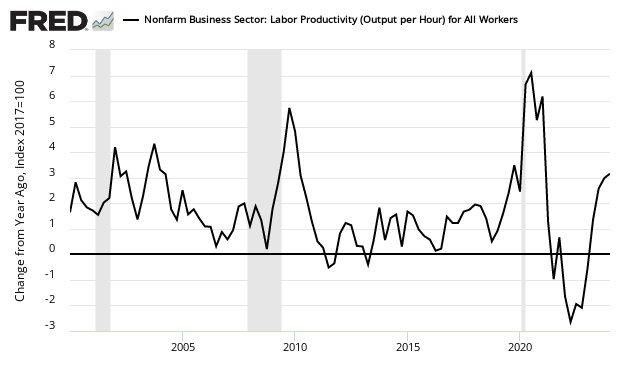
All this is happening while business sector unit labor costs increased.
Seasonally Adjusted Year-over-Year Rate of Change of Unit Labor Costs
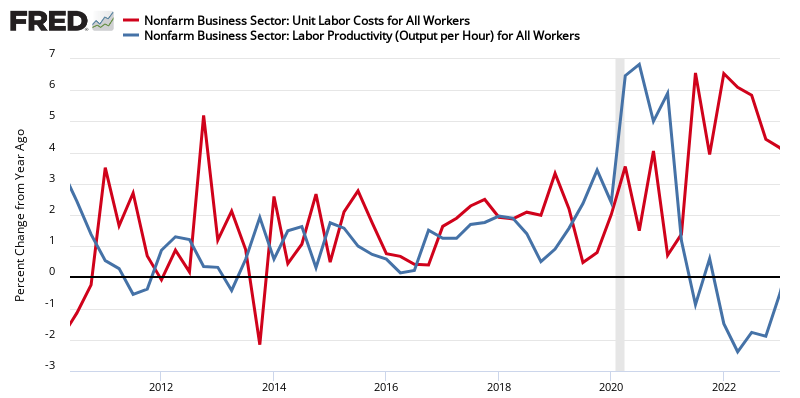
The headlines from the press release:
Nonfarm business sector labor productivity increased 2.3 percent during the third quarter of 2018, the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics reported today, as output increased 4.1 percent and hours worked increased 1.8 percent. (All quarterly percent changes in this release are seasonally adjusted annual rates.) From the third quarter of 2017 to the third quarter of 2018, productivity increased 1.3 percent, reflecting a 3.7-percent increase in output and a 2.3-percent increase in hours worked.
Unit labor costs in the nonfarm business sector increased 0.9 percent in the third quarter of 2018, reflecting a 3.1-percent increase in hourly compensation and a 2.3-percent increase in labor productivity. Unit labor costs also increased 0.9 percent over the last four quarters.
Preliminary Chart for 3Q2018

Final Chart for 3Q2018

My view of Productivity
My view of productivity is very different from the headline view. Productivity is complicated - far too complicated for economists to come to a conclusion satisfactory to this simple Industrial Engineer:
Generally speaking, productivity is, in industrial engineering, defined as the relation of output (i.e. produced goods) to input (i.e. consumed resources) in the manufacturing transformation process.
Productivity assessments even within a single company are very complicated and are impossible to accurately forecast when one wants to discuss an entire sector or economy. There are some rough tools which will get one into the ballpark of productivity improvement. The following graphs on manufacturing, investment, retail trade and health care are comparing inflation-adjusted growth of that sector to employment growth in that sector - as well as for the economy overall.
In the case of the economy overall, output (blue line) and employment are now growing at the same rate.

In the case of manufacturing, output (blue line) and employment are now growing at the same rate. Prior to the Great Recession, output grew whilst employment fell.
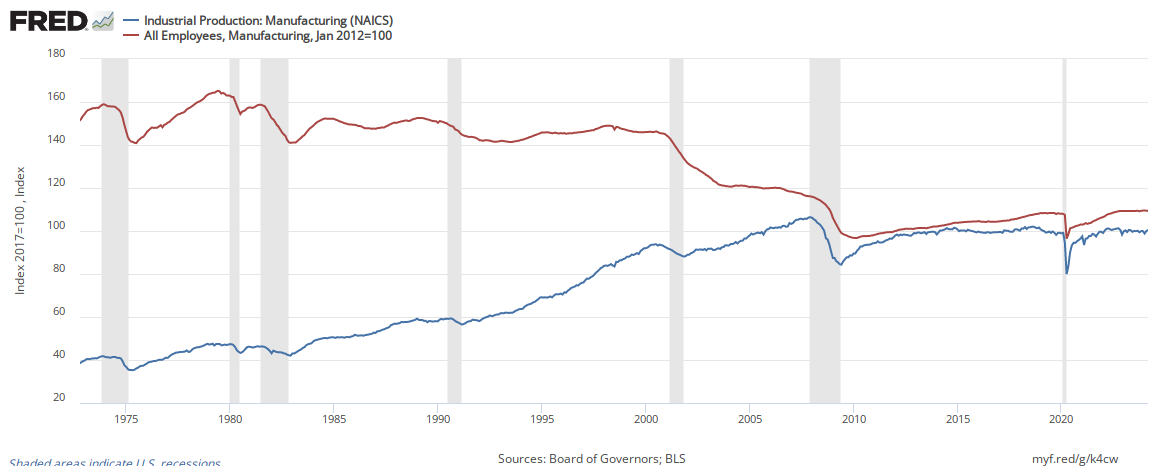
The above chart is saying there is no productivity growth in manufacturing - even with our belief that robotics are doing away with jobs.
A slightly different situation is true with construction. Since 2012, construction output and employment are growing at the same rate implying there is no productivity growth. But during the Great Recession and its immediate aftermath, productivity appears to have declined.

The only real productivity growth I can find is in the services sector. Beginning with the retail sector, the obvious gain in productivity is seen throughout the graph below and continues today.

There is also improvement in the health care sector.

The above look at productivity is down and dirty - but it should provide a realistic ballpark productivity assessment. Real productivity should not have significant fluctuations except during recessions which makes one skeptical of the headline view.
Another way of looking at productivity is the year-over-year rate of growth of GDP per employed population - red line) vs. GDP per capita (blue line). This metric is partially showing how well business is utilizing the labor force - and in a rough way looks at productivity growth if one eliminated government transfer payments from GDP. (see red line in graph below):

The above graph suggests productivity growth is roughly 1.1 % per year. This analysis also suggests for the last two years, the health of the economy has been improving.
The problem really is that economists only understand money flows - and how they got into measuring productivity is beyond my comprehension. This is an extremely nuanced calculation which is never totally accurate as you are shifting technology or methods. but the core of industrial engineering is a measure of labor hours - and that is foreign to the way the BLS measures productivity.
As one outsources, one would expect labor hours to drop - and that should be relatively accurate.
But the prime reason one is driven to optimize productivity is profits. when a methodology to improve productivity is considered, this calculation is about costs - how much does it cost to get the productivity gain.
Now the spoiler today is likely logistics - as robotics mean that one can produce a product literally anywhere in the world (so labor cost is no longer the prime factor - although pollution is and many processes are inherently dirty). Logistics becomes the primary element which means manufacturing is coming back to the USA.
But as new manufacturing re-appears, the labor growth is likely equal to product output (as the old labor-intensive technologies were exported and what was left was productivity efficient).
Caveats Relating to Productivity
Productivity is determined using monetary criteria, and does not recognize outsourced man hours - in other words, if a business cuts half of its workforce by outsourcing a sub-component or sub-service, this would be a 50% productivity improvement.
These productivity measures describe the relationship between real output and the labor time involved in its production. They show the changes from period to period in the amount of goods and services produced per hour. Although these measures relate output to hours at work of all persons engaged in a sector, they do not measure the specific contribution of labor, capital, or any other factor of production. Rather, they reflect the joint effects of many influences, including changes in technology; capital investment; level of output; utilization of capacity, energy, and materials; the organization of production; managerial skill; and the characteristics and effort of the work force.
Econintersect believes a better measure (if you must use monetary tools to tract productivity) would be competitiveness.
Looking at productivity/output long term - output fall below 0% year-over-year change is a good sign that a recession is underway. Another way to look at it - if productivity rate of gain is falling, this could be an indicator a recession is coming.
Disclaimer: No content is to be construed as investment advise and all content is provided for informational purposes only.The reader is solely responsible for determining whether any investment, ...
more


