Risk Blackout
In financial euphoria episodes, investors become immune to the risks of capital destruction by blacking out to their normal risk aversion. Usually, these episodes come from extrapolating the recent past out many years into the future. What can we learn from other disciplines about blacking out? How did this happen with investors in the past and where are risks in the U.S. stock market blacked out today?
In his most recent book, Talking with Strangers, Malcolm Gladwell explains how intoxication from alcohol moves as blood alcohol levels rise. At somewhere around .14 to .15, intoxication moves to what can be described as a ‘blackout’. The person is active and functioning but is not conscious of what they are doing. He discusses the terrible mistakes young people make in college from becoming overly intoxicated at these levels.
Over my forty years of investing, there have been multiple episodes of investor blackouts. As the chart below shows, my first experience was in gold, oil and other inflation beneficiaries circa 1981:
(Click on image to enlarge)
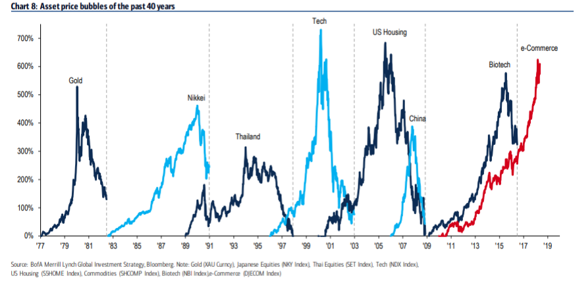
Source: DoubleLine Funds, BofA Merrill Lynch Global Investment Strategy, Bloomberg. Data for the time period 1/1/1977 – 12/31/2018.
Inflation was running at 11% as 79 million baby boomers were forming households, buying houses, cars and having children. Too much money was chasing too few goods and prices were overwhelmed. Investors moved nearly all their money into inflation hedges and short-term interest-bearing securities and blacked out to the risk of doing so. Equity ownership among households dropped to 10% of total household assets and the energy sector of the S&P 500 Index reached 28% of the total market cap. Inflation investments were completely intoxicating, and investors were blacked out to the risk of extrapolating the recent trend. Gold and oil plummeted in price for the subsequent 18 years.
The two pinnacles of intoxication were in the Dot-Com episode in the late 1990s and the residential real estate bubble of 2002-2006 (see the chart above). Price-to-earnings ratios for popular tech stocks were measuring the investor’s euphoric blood alcohol level. The neat thing about these blackouts in financial euphoria is that they severely damage capital for a long time regardless of whether the original premise being extrapolated was correct. The internet did change our life (Dot-Com) since 1999, but we didn’t need the homes built in 2004-2006.
What risks are we blacked out to today? First, inflation and interest rates have been very low for a very long time. This obviously puts bond investors at great risk since bond prices move inversely to interest rates. This is almost the antithesis of 1981. Second, all investments today are priced off discount rates that are the lowest of our lifetimes. As a result, people are paying way too much when extrapolating the future of the most successful companies of the last ten years. We all wished we’d have owned Visa, Mastercard, Nike, American Tower, Starbucks, Costco, Amazon, Netflix, PayPal, and other glamour growth stocks in the last ten years. This happened as investors became intoxicated with the combination of earnings growth and price-to-earnings ratio expansion from lower and lower discount rates.
However, that intoxication level is now blacking people out as investors are drinking glasses of indexes, momentum ETFs and low volatility ETF cocktails. See the money flows toward the decade long darlings below:
(Click on image to enlarge)
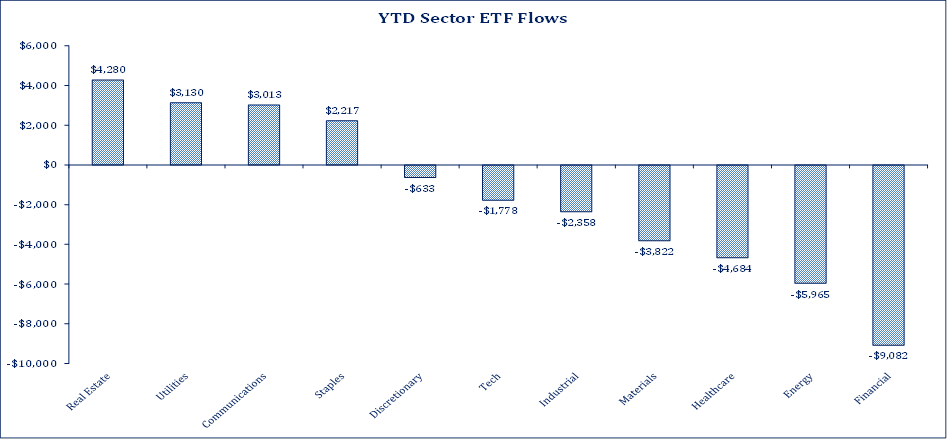
Source: Strategas
I can almost see the “Lost in Space” robot waving his arms and screaming, “danger, danger!” Growth stocks are valued 65% above the average of the last 67 years, while value stocks are 6.3% cheaper than the 67-year average even though stocks have gone up for ten years.
The irony of all of this is the same forces which blacked investors out in the inflationary episode of 1981, are preparing to do a mini-reverse replay and crush those blacking out from the blood alcohol euphoria level provided by low inflation today. In the 1970s and 1980s, 79 million boomers borrowed money to buy houses from 44 million silent generation saver/homeowners. Today, there are 90 million millennials who are going to borrow money to buy houses from 65.8 million Generation X saver/homeowners.
We believe it is time to sample cocktails among investments that do well as households are formed, economic activity picks up, inflation arises, and inflation hedge investments become pleasantly intoxicating. In 10 to 15 years, we hope to warn you when investors get blacked out to the new risks which get created in the process.
Disclosure: This article contains information and opinions based on data obtained from reliable sources, which is current as of the publication date, and does not constitute a recommendation ...
more


