Copper: Inducing A Sustainable Future
What’s the secret behind the eternal youth of Lady Liberty standing tall in New York for over a century?
The same dynamic element that has been used by humans for over 10,000 years: copper.
The French knew copper would be the ideal element for the Statue of Liberty’s outer layer—being lightweight, rustproof, and strong but easy to shape—when they crafted it as a gift to the U.S. in 1886.
Today, copper is considered the bellwether for the global economy. It is used extensively in electronic devices, electricity delivery and storage, transportation, communication, and manufacturing.
Many of its industrial applications are geared for exciting long-term growth, which makes copper immensely promising as a thematic investment opportunity.
Let’s look at a few of those applications.
Copper Is Driving the Electric Vehicle Revolution
Copper is prevalent in three key areas of electric mobility: energy storage, charging infrastructure, and vehicle production.
According to the International Copper Study Group (ICSG), electric vehicles (EVs) use approximately four times more copper than cars with internal combustion engines.1 Wood Mackenzie expects global EV sales to rise from 5% of all vehicle sales today to 50% by 2040.2
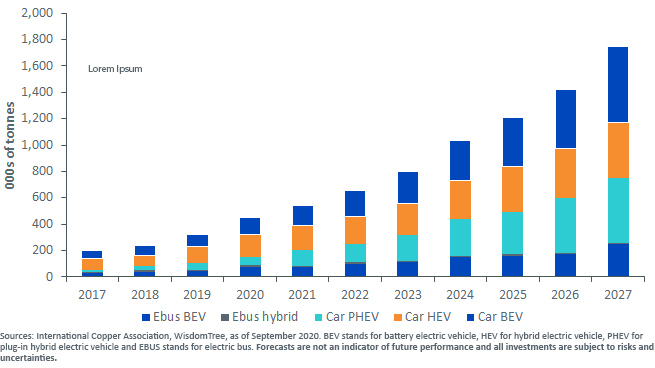
This technological revolution is thus expected to invigorate the demand for copper. Copper demand in EVs could increase by a multiple of four within the next seven years (see figure 1 below).
Figure 1: Copper Demand From Electric Vehicles is Poised for Growth
Copper Is Powering Smart Cities
Smart cities are employing new information technology solutions to solve urban problems of housing, transportation, energy, and governance.
Examples of smart city applications include the deployment of smart traffic lights that use predictive analytics to improve traffic flow; smart buildings to improve energy efficiency, safety, and security; and the development of 5G Internet connectivity to promote the Internet of Things economy—a state in which multiple smart devices are interconnected.
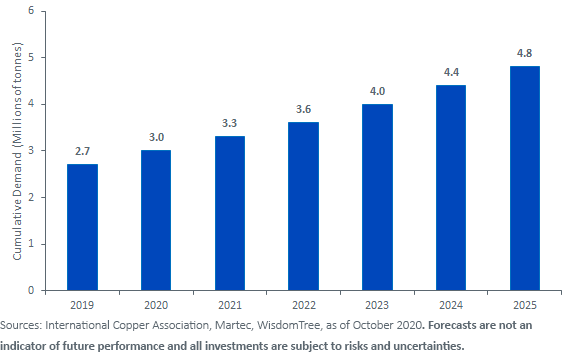
From smart grids to air conditioning systems, and EV charging infrastructure to 5G optical fibers, copper’s demand is expected to grow to enable the development and efficient running of smart cities (see figure 2).
Figure 2: Smart Cities are Expected to Demand Increasing Amounts of Copper
Copper Is Electrifying the Shift Toward Renewable Energy
Copper’s strong conductivity makes it an indispensable component of renewable energy power generation systems such as solar, wind and hydro generators to achieve optimum efficiency in power generation and transmission. It helps reduce carbon dioxide emissions and lowers the amount of energy needed to produce electricity.
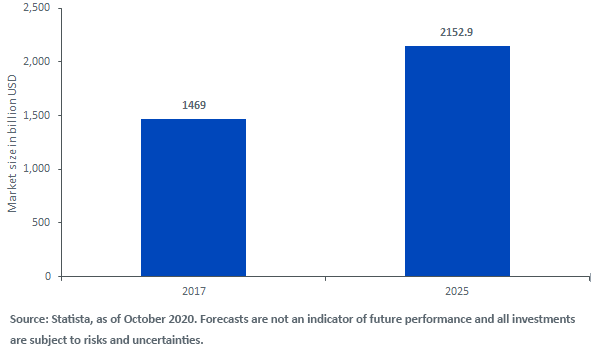
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), the world will add nearly 200 Gigawatts (GW) of renewable electricity capacity in 2021, up from just over 50 GW of new renewable electricity capacity added in 2007.3 For the expected growth in the renewable energy market to gather charge (see figure 3), greater quantities of copper will be required.
Figure 3: Global Renewable Energy Market is Expected to Continue Growing
Doing it All Sustainably
When it comes to sustainability, there are two questions to ask: is there enough copper on earth to meet the growing demand, and is the use of copper good for the environment?
The answer to both questions is a resounding yes.
According to ICA, the world has, on average, had 40 years of copper reserves since the 1950s.4 The U.S. Geological Survey of 2019 estimates global copper reserves at 830 million tonnes, copper resources in excess of five billion tonnes, and annual copper usage at around 28 million tonnes. Copper can also be recycled repeatedly without losing its physical properties. Around one-third of all copper used, today is recycled.
Markets Are Recognizing Copper’s Potential
Copper has been leading the way among industrial metals since the recovery in cyclical assets gathered pace in March 2020. This is partly attributable to COVID-19-related supply disruption from key mining countries like Chile causing the supply deficit to widen in the first half of this year (according to ICSG). But it is also because industrial metals with long-term prospects benefit from cyclical as well as structural tailwinds.
WisdomTree recently re-weighted our WisdomTree Enhanced Commodity Strategy Fund (GCC) to include a structural over-weight to copper and industrial metals more broadly.
These positions are motivated by our view of the importance of this megatrend rise in battery metals.
1https://www.copper.org/publications/pub_list/pdf/A6191-ElectricVehicles-Factsheet.pdf
2https://www.woodmac.com/our-expertise/capabilities/electric-vehicles/
3https://www.iea.org/reports/renewables-2020/renewable-electricity-2#abstract, as of November 2020.
4https://copperalliance.org/about-copper/long-term-availability/, International Copper Alliance (ICA), as of 2020.
Disclaimer: Investors should carefully consider the investment objectives, risks, charges and expenses of the Funds before investing. U.S. investors only: To obtain a prospectus containing this ...
more